Have you ever watched a child mix blue and yellow paint, their eyes wide with anticipation as they blend the colors together? The act of mixing colors seems intuitive, almost magical, yet it hides a complex world of pigments, light, and the way our eyes perceive color. Today, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of color mixing, uncover the secrets behind blue and yellow, and explore the captivating journey of creating a vibrant green.
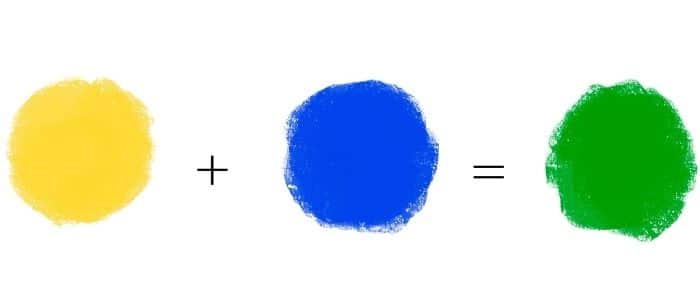
Image: artstudiolife.com
We all have an innate understanding of the basic color wheel, learning early on that combining blue and yellow yields green. But what happens in the realm of pigments when these colors meet? What are the nuances of green, and how can we achieve the perfect shade for our artistic creations or understand the intricate workings of nature’s palette?
A Journey Through Pigment Mixing
When we mix blue and yellow paint, we are actually combining pigments, tiny particles that absorb certain wavelengths of light and reflect others. This process determines the color our eyes perceive. Blue pigments, for instance, tend to absorb most wavelengths except for those in the blue region of the visible spectrum, which they reflect back to our eyes. Similarly, yellow pigments absorb most wavelengths except for those in the yellow region, reflecting them back.
As we blend these pigments, we create a new mixture that absorbs a greater range of wavelengths. The missing wavelengths, those reflected by both blue and yellow, are mainly in the green portion of the spectrum, resulting in a green hue. The shade of green we achieve depends on the precise hues of blue and yellow employed. A vibrant, electric yellow will produce a brighter green, while a muted, ochre yellow will create a more earthy green. Similarly, a cool blue like cerulean will result in a cooler green, while a warm blue like ultramarine will contribute to a warmer green.
Beyond the Paint Palette: Nature’s Green
The magic of color mixing isn’t limited to our art supplies. In the natural world, the vibrant greens of foliage arise from a complex interplay of pigments within the leaves of plants. Chlorophyll, the essential pigment for photosynthesis, absorbs most light wavelengths except for those in the green region, which are reflected back, giving plants their characteristic green color. Different plant species exhibit varying shades of green, from the deep emerald of ancient forests to the shimmering lime of newly-sprouted leaves. These differences are influenced by factors like the type of chlorophyll present, the presence of other pigments like carotenoids and anthocyanin, and the level of light exposure.
The Science of Green
While pigments and light play crucial roles in color mixing, our perception of color is equally important. The human eye contains receptors called cones, which detect different wavelengths of light. When we look at a green object, cones sensitive to green wavelengths are stimulated, leading us to perceive that object as green. However, our perception of green is subjective and can be influenced by a variety of factors. For instance, the color of surrounding objects can affect our perception, leading us to view the same green differently under different lighting conditions.
Image: nz-avto.ru
Green Through the Ages
Throughout history, green has held cultural and symbolic significance. In ancient Egypt, green represented growth, fertility, and life. In the Renaissance, green was associated with wealth, prosperity, and the power of nature. Today, green continues to evoke a sense of serenity, harmony, and renewal, often associated with environmental consciousness.
The Art of Creating the Perfect Green
Whether you are a seasoned artist or an aspiring painter, understanding how to mix blue and yellow to achieve the perfect shade of green is a valuable skill. Experimentation is key, as different brands of paint can produce varying results. Start by mixing a small amount of blue and yellow on your palette, gradually adjusting the ratio to achieve the desired shade. Remember that a touch of white can lighten a green, while a bit of black can deepen it. Don’t be afraid to explore different shades of blue and yellow, mixing cool tones with warm tones to create a variety of greens that reflect the complexities of the natural world.
Expert Insights: Unveiling the Secrets of Green
Artists often have their own unique methods for achieving specific shades of green. Renowned watercolorist, Paul Cézanne, famously favored a muted, earth-toned green, often using a combination of French ultramarine blue and cadmium yellow. Conversely, abstract expressionist painter, Mark Rothko, was known for his vibrant, almost luminous green hues, achieved by layering thin washes of different blue and yellow pigments. Both artists demonstrate that the beauty of green lies in its versatility and adaptability.
Embrace the Green Within: From Art to Nature
Now that you’ve unlocked the secrets of mixing blue and yellow, you can experiment with color theory and harness the power of green in your own artistic endeavors. Whether you’re painting landscapes, creating abstract masterpieces, or simply adding a touch of color to your home, embracing the versatility of green allows you to express your creativity and connect with the wonders of the natural world.
What Color Does Blue And Yellow Make
https://youtube.com/watch?v=70zrmAQPPao
Conclusion
The magic of color mixing, particularly with blue and yellow, lies not only in the vibrant green we create but also in the understanding of pigments, light, and perception it unlocks. As you explore the world of color, remember that green isn’t just a color; it’s a journey, a testament to the beauty of the natural world, and a conduit for our artistic expression. So, pick up your brushes, embrace the creativity within you, and let the magic of color mixing guide you on a journey through the vibrant spectrum of green. And don’t forget to share your artistic creations with us, we would love to see the green you create!






