Have you ever wondered about the peculiar endings tacked onto the titles of legal documents and journal articles? While they might seem like an arcane formality, these suffixes actually hold clues about the type, purpose, and even the history of the text they accompany. From the familiar “Jr.” at the end of a name to the rarely seen “et al.” in a legal citation, these seemingly insignificant additions offer a window into the world of legal and academic writing.
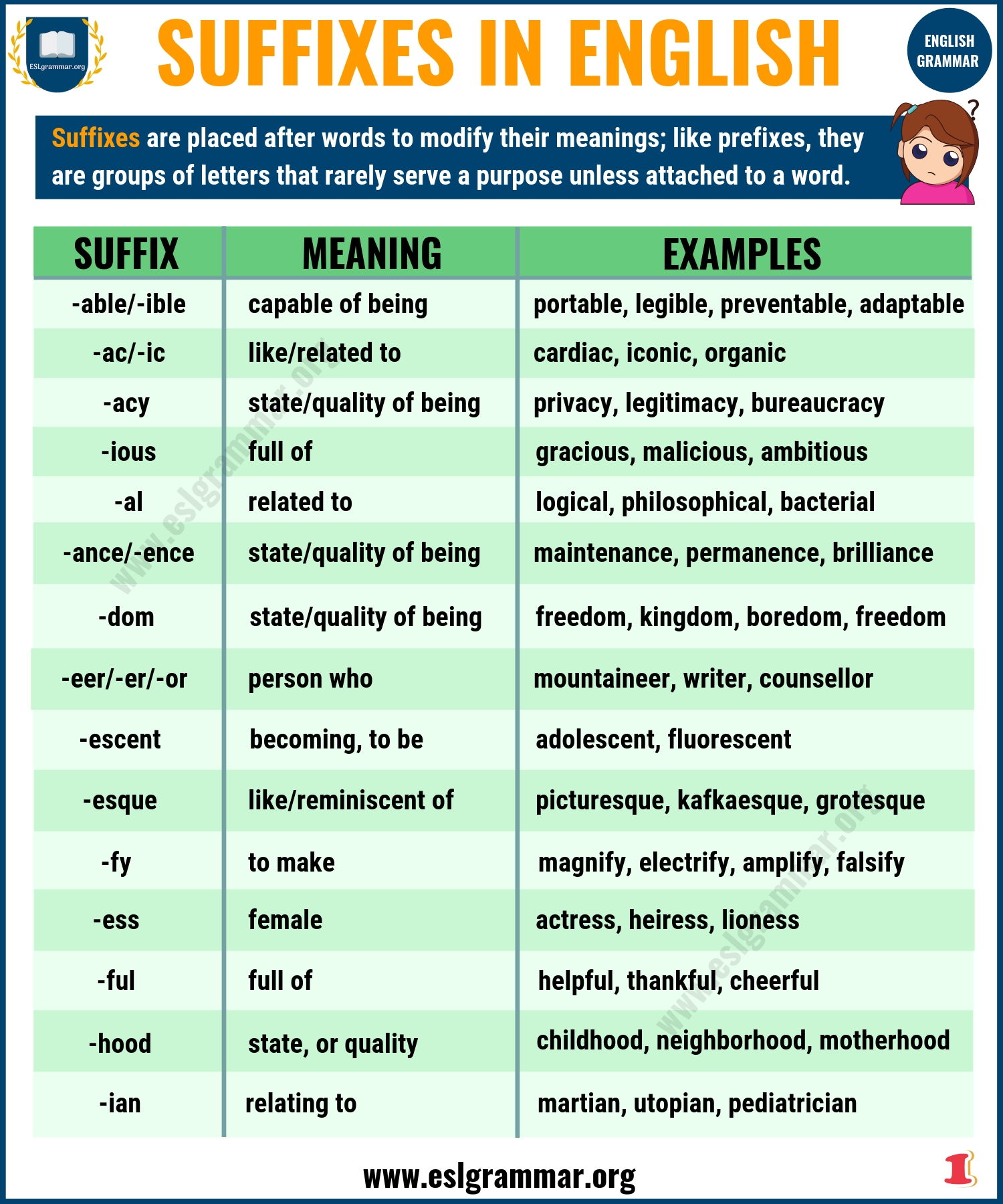
Image: eslgrammar.org
Understanding these suffixes is not just a matter of intellectual curiosity. They can significantly affect your ability to navigate legal documents, interpret scholarly articles, and even understand the nuances of communication within specific fields. Whether you’re a legal professional, a student, or simply someone interested in the workings of the legal and academic worlds, knowing the language of suffixes can unlock deeper meaning and understanding.
Common Suffixes in Legal Documents
The world of legal documents is populated by a unique set of suffixes, each with its own specific meaning. Here are some of the most common ones you might encounter:
- Jr. (Junior) and Sr. (Senior) – These suffixes distinguish individuals with the same name within a family. They indicate the younger or older generation. Example: John Smith Jr. vs. John Smith Sr.
- II, III, IV, etc. – These Roman numerals are used similarly to Jr. and Sr. to differentiate individuals with the same name, typically within a lineage. Example: William Jones III, indicating the third generation bearing the name William Jones.
- Esquire (Esq.) – This suffix was historically a title given to lawyers or gentlemen. While its usage is waning, it still appears in legal documents, particularly in traditional legal settings or when referring to attorneys. Example: Jane Doe, Esq.
- In Re – This Latin phrase translates to “in the matter of” and indicates a legal matter, often a probate case or bankruptcy case. Example: In re the Estate of John Doe.
- Ex Parte – This phrase, meaning “from one side,” identifies a legal action taken by one party without notice to the other. Example: An ex parte motion seeking a temporary restraining order.
- et al. – This abbreviation comes from the Latin “et alii,” meaning “and others.” It is used in legal citations when a legal document has multiple authors. Example: Smith et al., 2023.
Suffixes Found in Journal Articles and Academic Texts
While legal documents have their own set of suffixes, journals and academic texts are also rich with these linguistic markers. Here are some notable examples:
- Ph.D./M.D./LL.D. – These suffixes indicate the highest levels of academic achievement in various fields: Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), Doctor of Medicine (M.D.), and Doctor of Laws (LL.D.). They are often placed after the individual’s name to signify their academic credentials. Example: Dr. Jane Doe, Ph.D.
- Eds. – Short for “editors,” this suffix indicates the editors of a book or journal. Example: Smith and Jones, Eds., The Journal of Legal Studies.
- No. or Vol. – These suffixes indicate the specific issue number or volume of a publication. Example: The Journal of Legal Studies, Vol. 20, No. 3.
- et al. – As in legal citations, this suffix is used in academic works to indicate multiple authors on a research paper or book. Example: Jones et al., “The Impact of Legal Reform on Legal Research.”
- Corp. or Inc. – These suffixes indicate a corporation, which is a legal entity separate from its owners. Example: Microsoft Corp. or Google Inc.
Unveiling the History Behind Suffixes
Many of the suffixes used in legal and journal titles have their roots in Latin and ancient legal traditions. The use of “Jr.” and “Sr.” for example, stems from a time when family lineage was a crucial factor in legal and social standing. Similarly, the phrase “In re” dates back to Roman law, highlighting the enduring influence of historical language on contemporary legal practice.
The suffix “Esq.” has also gone through fascinating transformations over time. Initially a title reserved for nobility, it later evolved to identify lawyers and those holding positions of significant social standing. Its continued presence in legal documents, though somewhat archaic, speaks to the legacy of these historical distinctions and the evolution of social norms.
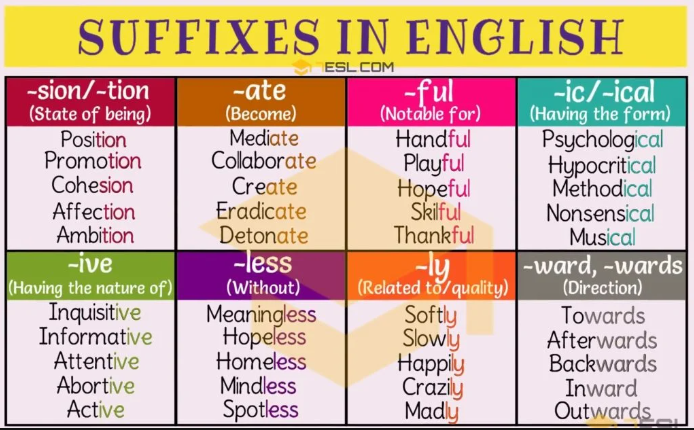
Image: www.gioinauan.com
Navigating the Complexities of Suffixes
While understanding suffixes is important, it’s crucial to recognize the nuances and potential for ambiguity. For instance, using “Jr.” in a legal document can lead to confusion if the individual’s father also shared the same name. Similarly, relying solely on “Corp.” or “Inc.” to identify a company might not be sufficient, as there might be multiple companies with the same name.
To avoid errors and ensure clarity, it’s important to consult additional sources of information, such as official records or databases. For example, when interpreting a legal document, referring to a court filing or deed could provide further context and resolve any ambiguity regarding individuals or entities.
The Future of Legal and Journal Suffixes
As language evolves and legal practice becomes increasingly globalized, the use of traditional suffixes may undergo further transformation. The emergence of digital platforms and online databases could lead to alternative methods of identifying individuals and entities, potentially diminishing the reliance on traditional suffixes.
Moreover, the increasing influence of international legal systems might lead to the adoption of new suffixes or the modification of existing ones to better reflect evolving legal and cultural practices. It’s an exciting time to observe the evolution of legal and journal titles, as they reflect the dynamic interplay between language, history, and modern practices.
Suffix For Legal Or Journal
Conclusion
Understanding the language of suffixes is a crucial step towards navigating the world of legal documents and journal articles. From the historical significance of “Esq.” to the practical importance of “In re,” these seemingly simple additions provide a window into the intricacies of legal writing and academic discourse. While traditional suffixes might evolve or even fade away, their role in conveying meaning and shaping the way we communicate within specific fields remains invaluable.
So, the next time you encounter a legal document or read a scholarly article, take a moment to appreciate the subtle power of suffixes. They’re more than just grammatical devices; they are the keys to unlocking a deeper understanding of legal and academic conventions, revealing the rich history and complex evolution of these fields.






