Have you ever felt a nagging pain in your lower back that just won’t quit? Or maybe you’ve experienced a sharp shooting pain that travels down your leg? If so, you might be dealing with a diffuse disc bulge, a common condition affecting the spinal discs, those shock absorbers that cushion your vertebrae.

Image:
Understanding diffuse disc bulges is crucial because they can significantly impact your quality of life. While not always a cause for alarm, they can lead to discomfort, pain, and limitations in your mobility. This article will delve into the intricacies of diffuse disc bulges, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By shedding light on this common spinal condition, we aim to equip you with knowledge to better understand and navigate the challenges it presents.
What is a Diffuse Disc Buldge?
Imagine a jelly-filled donut; the jelly represents the nucleus pulposus, the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc. The donut itself represents the annulus fibrosus, the tough outer layer that holds the nucleus together. When a disc bulges, this outer layer stretches and weakens, causing the nucleus to bulge outward, pushing against the nearby nerves.
A diffuse disc bulge is a specific type of disc bulge where the outward protrusion is not localized to one area but spreads out across a wider section of the disc. This expansive bulge can put pressure on the surrounding nerves and spinal cord, leading to various symptoms depending on the affected area.
Causes of Diffuse Disc Bulges
Diffuse disc bulges are often attributed to age-related wear and tear. As we age, the discs naturally lose their water content, becoming less flexible and more prone to bulging. Other factors contributing to disc bulges include:
- Repetitive stress: Certain occupations or activities that involve repetitive lifting, twisting, or bending can place excessive strain on the discs, increasing the risk of bulging.
- Trauma: Accidents or injuries, such as a car accident or a fall, can lead to sudden pressure on the discs, causing them to bulge.
- Poor posture: Maintaining a poor posture for extended periods can exert uneven pressure on the spine, weakening the discs and making them more susceptible to bulging.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added strain on the spine, increasing the likelihood of disc bulges.
- Genetics: A predisposition to disc problems might run in families, making some individuals more prone to developing diffuse disc bulges.
Symptoms of a Diffuse Disc Buldge
The symptoms of a diffuse disc bulge can vary depending on the location of the bulge and the extent of nerve compression. Common symptoms include:
- Back pain: Often described as a dull ache or sharp pain that worsens with movement, lifting, or standing for long periods.
- Pain radiating down the leg: This is known as sciatica and can be characterized by a burning, tingling, or shooting pain that extends from the buttocks to the foot.
- Numbness or tingling: This sensation can affect the leg, foot, or even the buttocks depending on the location of the bulge.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the leg or foot can occur due to nerve compression.
- Difficulty with bowel or bladder control: In rare cases, a large disc bulge can compress the nerves controlling these functions, leading to incontinence. This is a serious symptom requiring immediate medical attention.
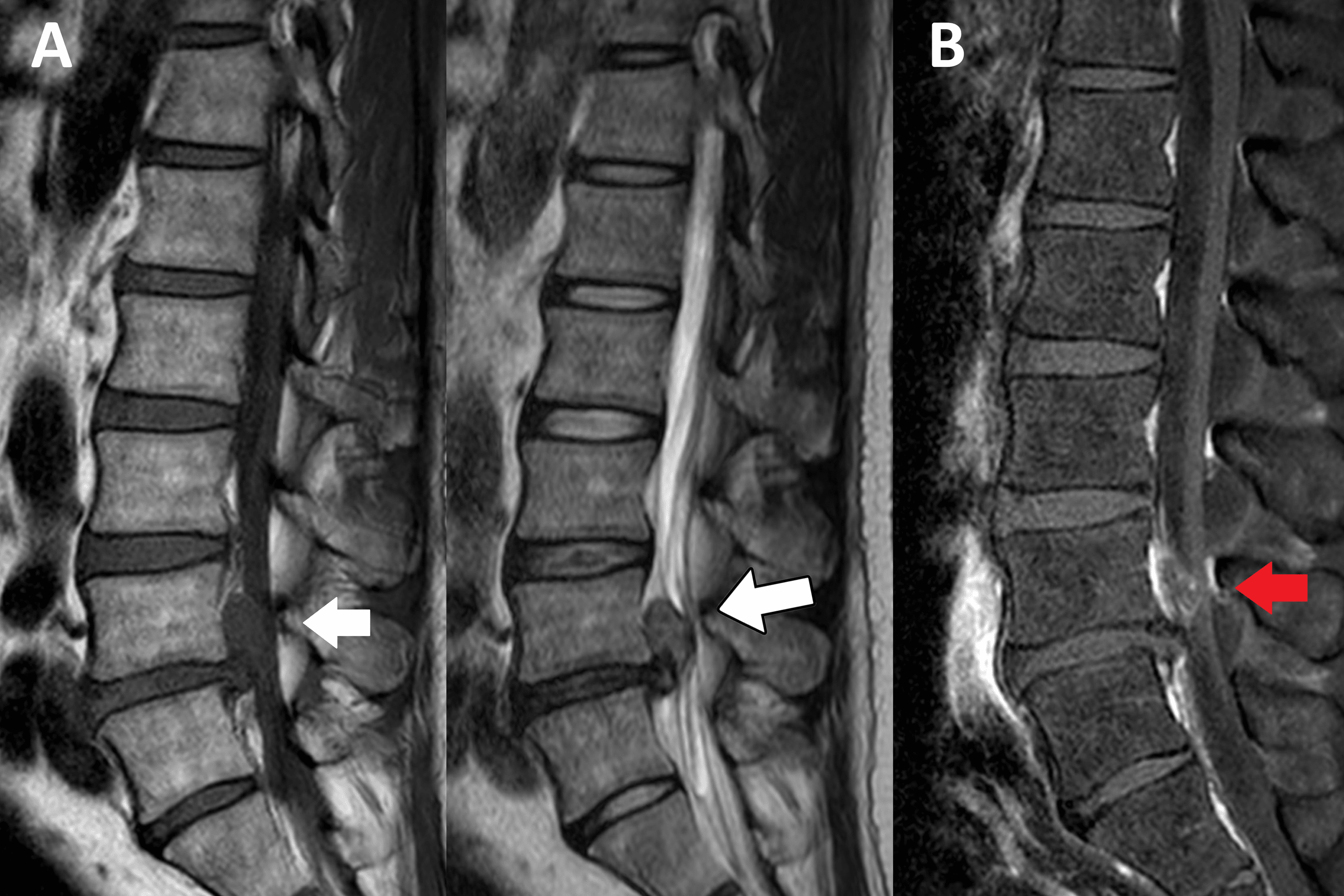
Image:
Diagnosis of a Diffuse Disc Buldge
Diagnosing a diffuse disc bulge typically involves a combination of physical examination and diagnostic tests. Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle habits. They will also perform a physical examination to assess your range of motion, reflexes, and neurological function.
Some common diagnostic tests used to confirm the diagnosis include:
- X-rays: These provide images of the skeletal structure and help identify any deformities in the spine. While X-rays can’t visualize soft tissues like discs, they can rule out other conditions.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This advanced imaging test provides detailed images of the spine, including the discs and surrounding structures, creating high-resolution images that enable doctors to identify disc bulging and any nerve compression.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: This scan often used alongside an MRI, offers detailed images of the bone and spinal canal, providing a clearer picture of the spinal structure and surrounding tissue.
- Myelogram: This test involves injecting dye into the spinal canal, followed by an X-ray or CT scan. The dye highlights the spinal cord and nerve roots, helping doctors visualize any bulges or nerve compression.
Treatment Options for Diffuse Disc Bulge
The treatment for a diffuse disc bulge depends on the severity of your symptoms and the extent of nerve compression. Mild cases may respond well to conservative treatments, while more severe cases might require surgery.
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments aim to reduce pain, inflammation, and improve overall function. These approaches include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that worsen the pain is important during the initial stages of a diffuse disc bulge. This allows the irritated nerves and muscles to heal.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger painkillers or muscle relaxants.
- Heat therapy: Applying heat to the affected area can help relax muscles and reduce pain. You can use a heating pad, hot water bottle, or even a warm bath.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen your back and core muscles, improve flexibility, and improve your posture. They may also recommend other therapies like massage or ultrasound.
- Injections: In some cases, your doctor may recommend injections of corticosteroids into the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Lifestyle modifications: Losing weight if you are overweight, improving your posture, and avoiding activities that trigger your symptoms can help prevent further disc damage and minimize pain.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases of diffuse disc bulge where conservative treatments have failed or when there is significant nerve compression causing weakness or incontinence. Surgical options include:
- Laminectomy: This involves removing part of the bone (lamina) covering the spinal canal, creating more space for the compressed nerve root.
- Discectomy: This procedure involves removing the bulging portion of the disc to relieve pressure on the nerve.
- Fusion: This surgery involves fusing two vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and prevent further disc bulging.
Preventing Diffuse Disc Bulges
While it’s not always possible to prevent diffuse disc bulges completely, several steps can reduce your risk:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra strain on the spine, increasing the risk of disc bulges. Losing even a few pounds can make a significant difference.
- Practice good posture: Proper posture distributes your weight evenly across the spine, reducing stress on the discs. Engage a physical therapist to identify your postural weaknesses and address them.
- Use proper lifting techniques: When lifting heavy objects, always bend your knees and lift with your legs, not your back. Avoid twisting while lifting.
- Regular exercise: Strength training and core exercises can strengthen the muscles that support the spine, preventing disc bulges.
- Stretching: Regular stretching keeps your back muscles flexible, reducing stress on the spine.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the discs, making them weaker and more prone to bulging.
Living With a Diffuse Disc Buldge
For many people, a diffuse disc bulge is a temporary condition that resolves with conservative treatments. However, it’s crucial to take steps to manage the condition and prevent worsening symptoms. This involves regular exercise, practicing good posture, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that trigger your pain.
If you’re experiencing persistent pain or any neurological symptoms, seek medical attention from your doctor. They can help diagnose the underlying cause of your pain and recommend the most effective treatment plan based on your specific situation.
Diffuse Disc Buldge
Final Thoughts
A diffuse disc bulge can be a challenging condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take control of your health and well-being. Remember that early diagnosis and treatment can improve your chances of a quicker and more successful recovery. If you suspect you might have a diffuse disc bulge, don’t hesitate to consult a medical professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.






