Have you ever woken up with a stiff neck or a sharp pain in your lower back that seemed to come out of nowhere? You might be experiencing the effects of a broad bulging disc, a common condition that affects countless individuals worldwide. While it may sound daunting, understanding the mechanics of a broad bulging disc and its associated symptoms can empower you to take control of your health and manage the discomfort.
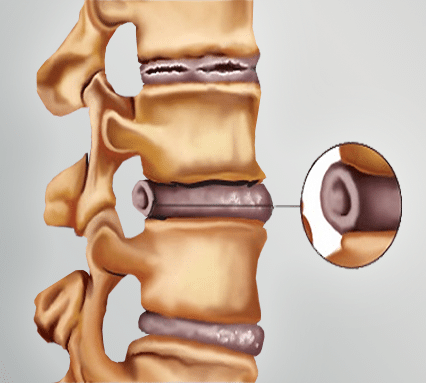
Image: www.spineorthocenter.com
A broad bulging disc, simply put, occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc pushes against the outer layer, causing it to bulge outward. These discs act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae in your spine, cushioning them and allowing for flexibility. A bulging disc can put pressure on nearby nerves, leading to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for a broad bulging disc, equipping you with knowledge to navigate this condition with confidence.
What is a Broad Bulging Disc?
The Anatomy of an Intervertebral Disc
To grasp the concept of a broad bulging disc, let’s first understand the anatomy of the intervertebral disc itself. It consists of two main components:
- Nucleus Pulposus: The soft, gel-like center of the disc. It’s primarily made of water and acts as a shock absorber.
- Annulus Fibrosus: The tough, fibrous outer layer that surrounds the nucleus pulposus. It provides structural support and helps contain the nucleus.
The Mechanism of Bulging
When the nucleus pulposus pushes against the annulus fibrosus, it can cause the outer layer to bulge outward. This bulging can be localized or broad, as in the case of a broad bulging disc, which involves a larger area of the disc protruding. This often happens due to weakened, worn-down, or damaged annulus fibrosus. This weakening can occur due to age, trauma, repetitive strain, or even genetics.
/GettyImages-99312322-7ceec8f1e3fd40759f7c8f06d8b6396d.jpg)
Image: www.verywellhealth.com
Causes of a Broad Bulging Disc
A variety of factors can contribute to the development of a broad bulging disc, including:
- Age: As we age, the intervertebral discs naturally lose water content, becoming thinner and more prone to bulging.
- Trauma: A sudden impact or injury to the spine, such as from a car accident or a fall, can damage the discs.
- Repetitive Strain: Jobs that require frequent bending, lifting, or twisting can put undue stress on the spine and lead to disc degeneration.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or standing in awkward positions can strain the spine and increase the risk of disc problems.
- Obesity: Excess weight places added pressure on the spine, accelerating disc deterioration.
- Genetics: Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to disc problems.
Symptoms of a Broad Bulging Disc
The symptoms of a broad bulging disc can vary greatly depending on the location of the bulging disc and the extent of nerve compression. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Localized pain in the back, neck, or legs. The pain may be sharp, shooting, or dull, and may worsen with movement or prolonged sitting.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of pins and needles or numbness in the arms, legs, or feet.
- Weakness: Difficulty with fine motor skills or muscle weakness in the affected limbs.
- Stiffness: Limited range of motion in the spine, making it difficult to bend, twist, or rotate.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess your range of motion, muscle strength, and reflexes to evaluate the extent of nerve involvement.
- X-ray: X-rays can reveal bone abnormalities but may not show a bulging disc.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides a detailed image of the spine and surrounding tissues. It’s the gold standard for diagnosing bulging discs.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Offers cross-sectional images of the spine and can help visualize bone and soft tissue structures.
- Conservative Management: In many cases, conservative measures can effectively manage a bulging disc.
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate your pain and allow your body to heal.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Heat can also be helpful to relax muscles.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles, improve posture, and enhance spinal flexibility can help alleviate pain and improve function.
- Muscle Relaxants: In some cases, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to relieve muscle spasms.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Steroids can be injected into the epidural space surrounding the spinal nerves to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there are signs of nerve compression or spinal instability.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts unnecessary strain on your spine.
- Practice good posture: Be mindful of your posture when sitting, standing, and lifting.
- Engage in regular exercise: Strengthening your core muscles and improving spinal flexibility can help support your spine and prevent further injury.
- Avoid activities that aggravate your pain: Listen to your body and avoid the activities that worsen your symptoms.
- Consider complementary therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and yoga may offer additional pain relief and stress reduction.
Diagnosis of a Broad Bulging Disc
To diagnose a broad bulging disc, a medical professional will typically conduct a physical examination, review your medical history, and order imaging tests.
Treatment Options for a Broad Bulging Disc
The treatment goals for a broad bulging disc are to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further damage. Treatment options may include:
Living with a Broad Bulging Disc
While a broad bulging disc can be a source of discomfort, it’s important to remember that many people with this condition can live fulfilling lives with proper management. By focusing on the following, you can improve your quality of life:
Broad Bulging Disc
Conclusion
A broad bulging disc can cause discomfort, but it doesn’t have to define your life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, you can take an active role in your health and make informed decisions regarding your care. Remember that proper diagnosis and management are crucial for effective pain relief and improved quality of life. If you are experiencing back pain or other symptoms that may be related to a bulging disc, consult with a healthcare professional to receive a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.






