Have you ever wondered about the difference between gigabytes and gigabits? You see these terms thrown around a lot when talking about internet speed, data storage, and even file sizes, but it can be confusing to know exactly what they mean and how they relate to each other. In the digital world, information is measured in bits, the smallest unit of data. So, what’s the difference between gigabytes (GB) and gigabits (Gb)? Understanding this distinction is crucial for making informed choices about your internet plan, data storage, and overall digital experience.

Image: race.com
Gigabytes and gigabits are both units of measurement, but they represent different aspects of digital information. A gigabyte measures the amount of data stored or transferred, while a gigabit measures the speed of data transfer. In essence, a gigabyte is the “what” – the size of something – while a gigabit is the “how fast” – the speed at which something is transferred. This analogy is often used to explain the distinction: if a gigabyte is a bottle of water, then a gigabit is the speed at which you pour that water into a glass.
Understanding the Basics: Bytes and Bits
Bits: The Building Blocks of Digital Information
Let’s start with the fundamentals. The smallest unit of data in a computer is a bit. A bit is a binary digit, represented as a 0 or 1, and it’s the basic building block of all digital information. It’s like a switch that can be either on (1) or off (0). Think of it as a single light bulb, either lit or unlit.
Bytes: Grouping Bits Together
To represent more complex information, bits are grouped together. A byte is a group of 8 bits, and it’s the basic unit of data storage. The byte is like a word, made up of several letters (bits). A single byte can represent a letter, a number, or a special character.
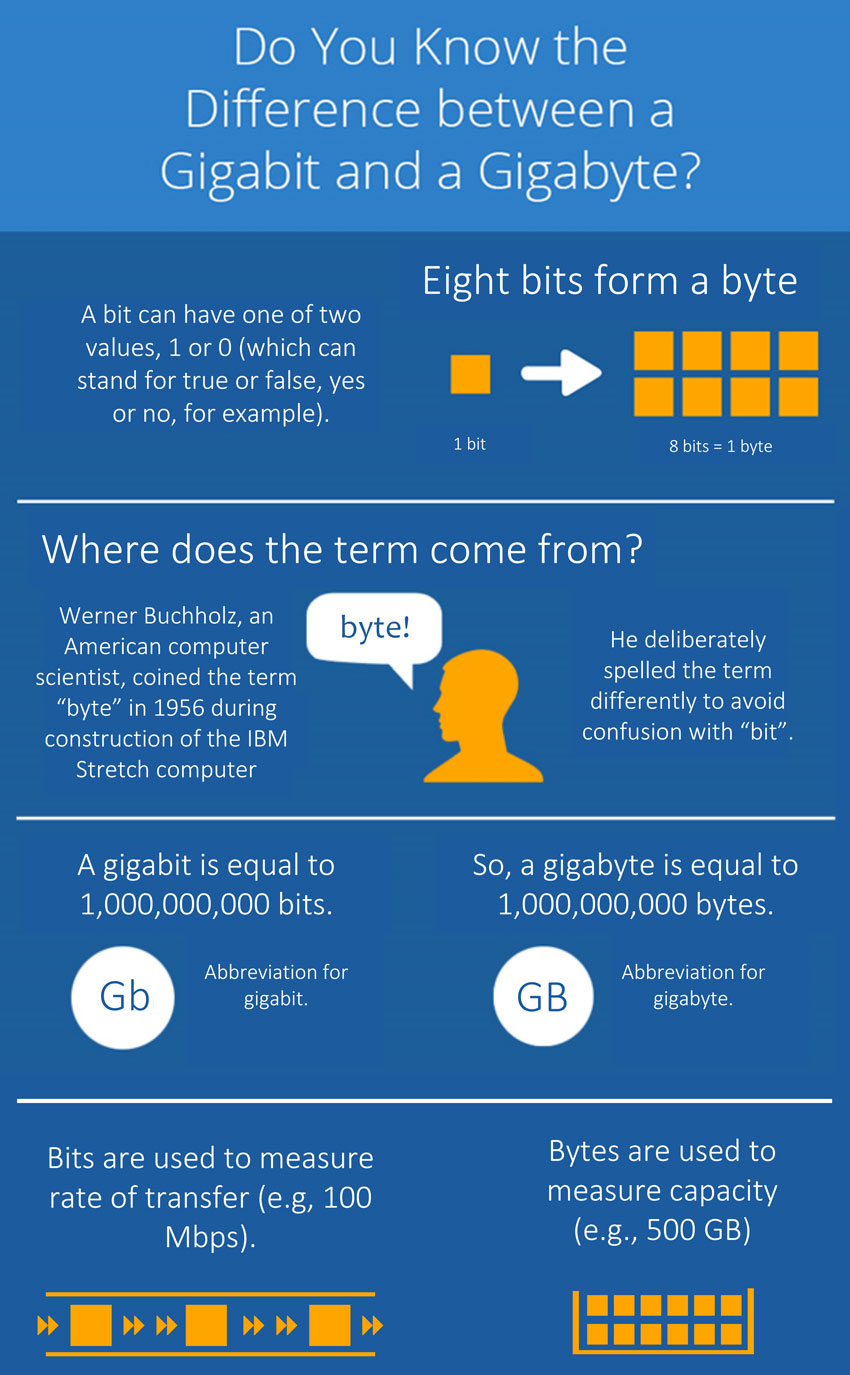
Image: www.atlantic.net
Gigabytes: Measuring Data Storage
A gigabyte (GB) is a unit of data storage that represents one billion bytes. It’s a common unit used to measure the capacity of hard drives, flash drives, and other storage devices.
Here are some real-world examples of gigabyte usage:
- A typical laptop hard drive may have a capacity of 500 GB.
- A high-resolution photograph might be around 10 MB (megabytes), or 0.01 GB.
- A full-length movie in high definition could easily consume 10 GB or more.
Gigabits: Measuring Data Transfer Speed
A gigabit (Gb) measures the speed of data transfer. It’s used to describe the rate at which data is sent or received over a network connection. One gigabit is equal to one billion bits per second.
- Broadband Internet: Internet service providers (ISPs) often advertise internet speeds in gigabits per second (Gbps). For instance, a 1 Gbps connection can theoretically transfer 125 MB of data per second.
- Data Transfer: When transferring files, the speed is measured in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s). This depends on the speed of your connection, the size of the file, and the network infrastructure.
- Data Storage Devices: Storage devices, like hard drives and SSDs, can also have transfer speeds measured in gigabits per second.
The Relationship Between Gigabytes and Gigabits
The key thing to remember is that gigabytes and gigabits are related but different. They’re not interchangeable.
- **Gigabytes measure the amount of data**, while **gigabits measure the speed at which that data is transferred.**
- **There’s a direct relationship:** The higher the bandwidth, measured in gigabits per second (Gbps), the faster you can download or upload files, measured in gigabytes (GB).
Why Does This Matter?
Understanding the difference between gigabytes and gigabits is essential for several reasons:
- Choosing the right internet plan: If you’re a heavy internet user, you’ll need a plan with a higher download speed (measured in Gbps).
- Streaming and download speeds: A faster internet connection will allow you to stream high-quality videos (4K or higher) and download large files more efficiently.
- Data storage needs: If you’re a photographer, videographer, or gamer, you’ll need ample storage space (measured in GB) to accommodate your files.
Gigabytes and Gigabits in the Real World
Let’s illustrate these concepts with real-world scenarios:
- Downloading a movie: Let’s say you want to download a movie that’s about 5 GB in size. With a 1 Gbps internet connection, it will take approximately 40 seconds to download. (Remember: 1 Gbps equals 125 MB/s). However, with a slower 100 Mbps connection, it might take 5 minutes or more.
- Streaming 4K video: Streaming high-quality 4K video requires a significant internet speed. You’ll need at least a 25 Mbps connection for a smooth streaming experience. With a 1 Gbps connection, you’ll have ample bandwidth even with multiple users streaming simultaneously.
Gigabyte Vs Gigabit
Conclusion
The distinction between gigabytes and gigabits might seem technical, but it’s crucial for understanding the digital world we live in. Gigabytes measure the storage capacity of our devices, while gigabits determine the speed at which we can move data across networks. Knowing this distinction allows you to make informed decisions about internet plans, data storage, and how to optimize your online experience. So, the next time you see these terms, you’ll have a clear understanding of what they mean and how they relate to your digital life.






