As someone who’s been through a fair share of surgical procedures, I know how crucial wound drainage systems are for a speedy recovery. After my recent knee surgery, my doctor opted for a Jackson-Pratt drain, and while it served its purpose, I couldn’t help but wonder about other alternatives like the Blake drain. With so many options available, it can feel overwhelming to navigate the world of wound drainage.
Image: www.primagem.org
This article will dive deep into the specifics of two popular drainage systems: the Blake drain and the Jackson-Pratt drain. We’ll explore their differences, advantages, and disadvantages to help you gain a better understanding of which might be best suited for your specific needs.
Understanding Wound Drainage Systems
The Role of Drainage in Wound Healing
Wound drainage systems play a vital role in promoting optimal wound healing by removing excess fluid, blood, and debris from the surgical site. This helps prevent infection, reduces swelling, and facilitates tissue regeneration. By drawing out these elements, drainage systems allow the wound to breathe and heal more effectively.
Types of Wound Drainage Systems
Numerous wound drainage systems are available, each with its own unique design and functionality. The choice of drainage system often depends on the type of surgery, the location of the wound, and the amount of drainage anticipated. The two systems we’ll focus on in this article, the Blake drain and the Jackson-Pratt drain, are both closed systems that utilize suction to facilitate drainage.
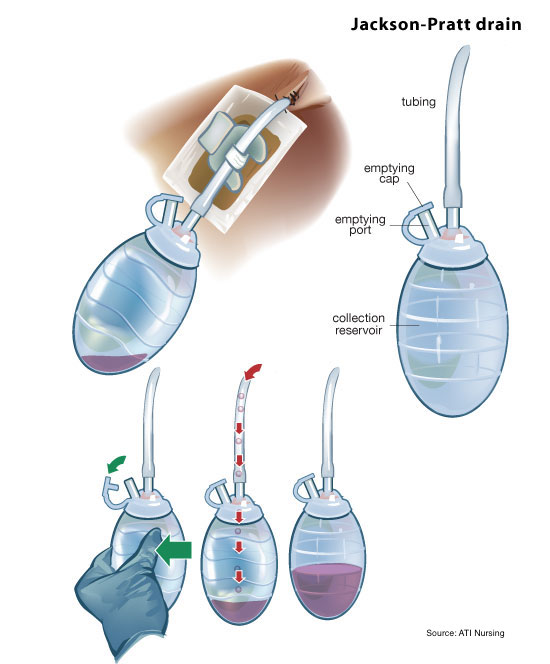
Image: masongardner.z19.web.core.windows.net
Blake Drain vs. Jackson-Pratt Drain: A Detailed Comparison
Blake Drain: A Comprehensive Overview
The Blake drain, also known as a “passive drainage system,” is a simple and cost-effective option that relies on gravity to promote drainage. It consists of a thin, flexible tube inserted into the surgical site and secured with sutures or adhesive tape. The tube is then attached to a collection bag positioned below the wound. The fluid flows passively from the wound into the collection bag, avoiding the potential need for suction.
Advantages of the Blake Drain:
- Simplicity: It’s easy to insert and remove, requiring minimal technical expertise.
- Cost-effective: Compared to the Jackson-Pratt drain, the Blake drain is generally less expensive.
- Minimal Discomfort: Its small size and passive drainage mechanism typically cause less discomfort for the patient.
Disadvantages of the Blake Drain:
- Limited Drainage: It might not effectively remove large volumes of fluid or thick exudate.
- Gravity Dependent: The drain relies on gravity to function, making it unsuitable for wounds located in areas where gravity doesn’t facilitate drainage.
- Risk of Leakage: Improper placement or dislodgement of the drain can lead to leakage of fluid outside the collection bag.
Jackson-Pratt Drain: An Active Drainage System
The Jackson-Pratt drain, often called a “closed suction system,” is a more complex system that utilizes suction to remove fluid from the wound. It comprises a bulb-shaped container connected to a drainage tube inserted into the surgical site. By compressing the bulb after emptying, a negative pressure is created, drawing fluid out of the wound and into the container.
Advantages of the Jackson-Pratt Drain:
- Effective Drainage: It efficiently removes significant volumes of fluid and thick exudate, even from deep wounds.
- Controllable Suction: The suction pressure can be adjusted based on the drainage needs of the wound.
- Minimal Leakage: Its closed suction system significantly reduces the risk of fluid leakage.
Disadvantages of the Jackson-Pratt Drain:
- Complexity: Requires proper insertion and manipulation, potentially requiring more technical expertise.
- Costlier: The Jackson-Pratt system tends to be more expensive than the Blake drain.
- Potential Discomfort: The suction pressure might cause discomfort in some patients.
Choosing the Right Drainage System: Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate drainage system depends on individual factors specific to each patient. Your doctor will consider several factors, including:
- Type of Surgery: Different types of surgeries require different drainage approaches.
- Location of the Wound: The location of the wound can influence the effectiveness of gravity-dependent drainage systems.
- Expected Amount of Drainage: The volume of drainage anticipated will determine whether a passive or active drainage system is necessary.
- Patient Preferences: Patient comfort and potential discomfort associated with each system should be considered.
- Cost: Budget constraints might influence the choice of drainage system.
Tips for Effective Wound Drainage
Proper management of your wound drainage system is essential for optimal wound healing and comfort. Here are some important tips to follow:
- Empty the Drainage Bag Regularly: Empty the collection bag frequently, typically every 4-6 hours, to prevent overflow and maintain negative pressure.
- Keep the Drainage Site Clean: Clean the area around the drain site with soap and water as instructed by your doctor.
- Secure the Drainage System: Ensure that the drain is securely attached to your skin and that the drainage tube is not kinked.
- Report Any Issues: Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual drainage, leakage, pain, or discomfort.
Expert Advice on Drainage Systems
Many medical professionals advocate for choosing the most appropriate drainage system based on a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s specific condition. This can often involve a detailed discussion about the advantages and disadvantages of each system and the patient’s individual preferences.
A patient should be involved in the decision-making process and feel confident in their understanding of the chosen system. This openness and transparency allow for a better patient experience. In cases where the doctor suggests a specific drain, it’s always beneficial to ask questions and express any concerns you may have about the chosen approach.
FAQ: Common Questions About Blake Drains and Jackson-Pratt Drains
Q: How Long Will I Need a Drain?
A: The duration of drainage depends on the type of surgery and the wound’s healing progress. Your doctor will typically remove the drain once the drainage volume has decreased significantly and the wound appears to be healing well.
Q: Is it Possible to Shower with a Drain?
A: In most cases, you can shower with a drain in place. However, it’s essential to keep the drain site dry and to follow specific instructions provided by your doctor.
Q: What Should I Do if the Drain Falls Out?
A: If your drain falls out, avoid inserting it back in. Contact your doctor or healthcare provider immediately to seek guidance and appropriate medical attention.
Q: What are the Warning Signs of Infection?
A: Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and a foul odor. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Q: How Long Does it Typically Take for the Wound to Heal After Drainage Removal?
A: Wound healing time varies greatly based on the size, complexity, and location of the wound. Your doctor will provide an estimated healing timeframe, but it’s essential to follow their instructions for optimal recovery.
Blake Drain Vs Jackson Pratt
Conclusion
Choosing between a Blake drain and a Jackson-Pratt drain can feel overwhelming. This guide has provided you with a thorough understanding of their features, advantages, and disadvantages to allow you to make an informed decision. Your doctor is the ultimate resource for determining the best option for your particular needs.
Are you interested in learning more about the latest advancements in wound care? Share your thoughts and let us know what you want to learn about next.






