Imagine this: you’re researching different hospitals for a loved one needing a critical procedure. One hospital boasts a low mortality rate, while another doesn’t even mention it. Which would you choose? It’s easy to see why mortality rates are so crucial in understanding a healthcare facility’s performance. But what exactly does the term “low mortality rate” mean, especially when it comes to conditions like heart disease, cancer, or even childbirth?

Image: www.researchgate.net
A low mortality rate paints a picture of a healthcare setting doing its best to save lives. But it’s crucial to understand the complexities behind this simple phrase. Beyond just numbers, a low mortality rate is a testament to skilled medical professionals, advanced technologies, and robust patient care practices. It’s a reflection of an institution’s dedication to delivering the highest quality of care.
Unveiling the Meaning Behind Mortality Rates
Defining the Term
A mortality rate, in simple terms, measures the number of deaths within a specified population over a particular period. It’s typically expressed as a percentage or a rate per 1,000 people. For example, a mortality rate of 5% for a specific disease would mean that 5 out of every 100 people diagnosed with that disease die within a certain time frame.
A **low mortality rate** indicates that fewer people are dying from a particular condition or within a specific healthcare setting. It’s a positive indicator of efficient medical intervention and effective patient management. Conversely, a **high mortality rate** suggests a greater number of deaths, potentially indicating issues with treatment effectiveness, diagnostic accuracy, or even underlying healthcare infrastructure.
The Importance of Context
Understanding the context of a mortality rate is crucial for accurate interpretation. For example, a low mortality rate for a specific type of cancer might be attributed to early diagnosis, advancements in treatment options, or even changes in risk factors within the population. It’s important to consider:
- Specific Disease or Condition: Mortality rates vary greatly depending on the disease or condition in question.
- Population Demographics: Age, gender, socioeconomic status, and preexisting health conditions can all influence mortality rates.
- Time Frame: Mortality rates are often calculated over a specific period, like a year or five years. This time frame can significantly impact the final figure.
- Geographical Location: Mortality rates can vary geographically, impacted by factors such as access to healthcare, environmental factors, and socioeconomic conditions.
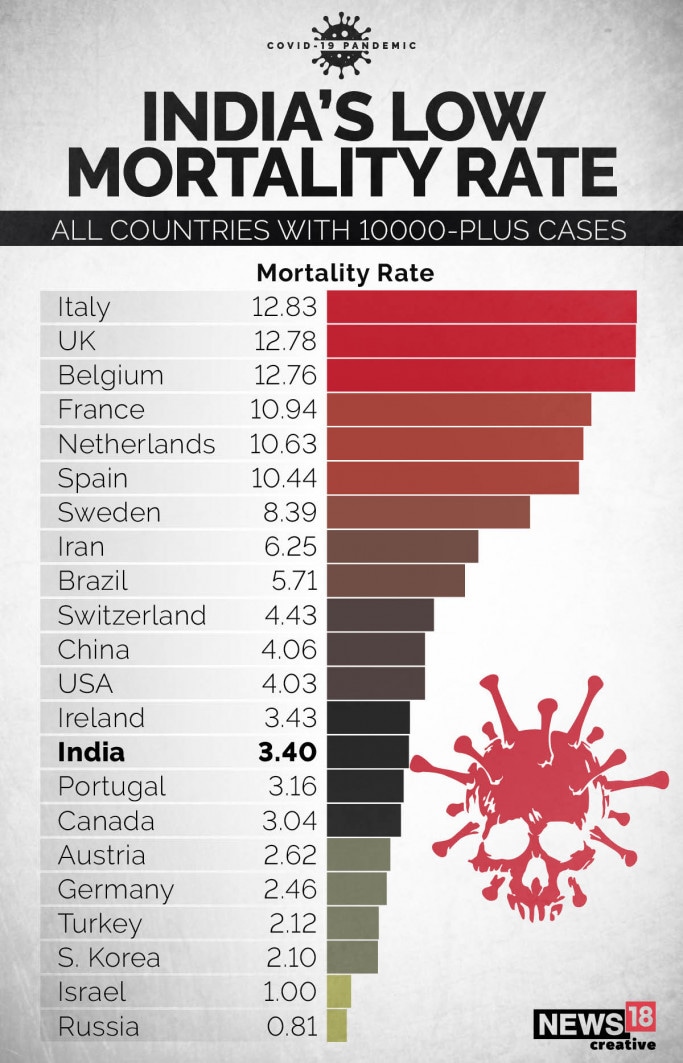
Image: www.news18.com
The Power of Comparison
Comparing mortality rates across different institutions or time periods can provide valuable insights. However, this comparison must be done with caution, ensuring that the data being compared is collected using similar methodologies and reflecting similar patient populations.
For instance, comparing a hospital’s mortality rate for heart attacks with a national average can highlight areas of strength or weakness. This data can help healthcare institutions identify areas for improvement and prioritize initiatives that can ultimately save lives.
The Evolving Landscape of Mortality Rates
The Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have played a significant role in improving healthcare outcomes and reducing mortality rates. New diagnostic tools, surgical techniques, and treatment modalities have revolutionized the way we treat a wide range of illnesses. For example, minimally invasive surgery, targeted therapies for cancer, and advanced imaging techniques have significantly improved patient survival.
Global Trends in Mortality Rates
Over the past few decades, global mortality rates have been steadily declining for many diseases. This decline is attributed to factors such as improved sanitation, access to clean water, widespread vaccinations, and increased investment in healthcare infrastructure. However, disparities in mortality rates still exist across different regions and socioeconomic groups, highlighting the need for continued efforts to improve healthcare access and quality globally.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite ongoing progress, challenges remain in tackling mortality rates. The emergence of new infectious diseases, antibiotic resistance, and aging populations present ongoing challenges to healthcare systems worldwide. Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining innovation, research, and collaborative efforts across different sectors.
The future of addressing mortality rates lies in harnessing the power of data analytics, personalized medicine, and predictive modeling. By analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns in healthcare outcomes, researchers can develop more effective interventions and personalized treatment plans that could potentially save countless lives.
Tips for Informed Decision-Making
When researching healthcare providers or information regarding a specific condition, it’s essential to consider more than just mortality rates. While a low mortality rate can be a positive indicator, it’s crucial to understand the factors that influence it and to consider other aspects of care, such as:
- Patient Satisfaction: How satisfied are patients with the care they receive at a particular facility?
- Experience and Expertise: What is the level of experience and expertise of the medical professionals at the facility?
- Technology and Infrastructure: What advanced technologies and resources are available at the facility?
- Patient-Centric Care: Does the facility prioritize patient-centered care and focus on individual needs?
By considering these factors in conjunction with mortality rates, you can make more informed choices regarding your healthcare. It’s also beneficial to seek multiple perspectives and to discuss your options with your healthcare providers.
FAQ
Q: Is a low mortality rate always a good sign?
A: While a low mortality rate generally indicates positive outcomes, it’s not always the sole indicator of a high-quality healthcare setting. Factors such as patient demographics, disease severity, and access to advanced treatments should also be considered.
Q: How can I find mortality rate information for hospitals or diseases?
A: Many government agencies and healthcare organizations publish mortality rate data for hospitals and specific diseases. You can often find this information on the websites of your state’s health department, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), or the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ).
Q: Can mortality rates be influenced by societal factors?
A: Absolutely. Access to healthcare, socioeconomic factors, living conditions, and environmental factors can all play a significant role in influencing mortality rates. Addressing these societal issues is crucial for improving health outcomes.
Q: What are some of the future challenges in reducing mortality rates?
A: Future challenges include the emergence of new diseases, antibiotic resistance, aging populations, and the potential for healthcare system vulnerabilities. Continual innovation, research, and a focus on preventive care will be essential in addressing these challenges.
What Does Low Mortality Rate Mean
https://youtube.com/watch?v=o7q0tXU5Pbw
Conclusion
Understanding the meaning of mortality rates can empower you to make informed decisions regarding your healthcare. While a low mortality rate certainly points to positive outcomes, it’s essential to consider the context, understand the complexity of this statistic, and evaluate other factors that contribute to overall quality of care. As we move forward, advancements in technology, data analytics, and personalized medicine hold immense promise for further reducing mortality rates and achieving better health outcomes for all.
Are you interested in learning more about this topic? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!






