Remember those days of juggling multiple operating systems on a single machine? The constant switching, the need for separate hard drives, the sheer complexity. It felt like we were always fighting against the limitations of our hardware. But then Intel brought us something revolutionary: VT-x and VT-d. These technologies are the backbone of modern virtualization, allowing us to run multiple operating systems seamlessly on a single machine, maximizing performance and efficiency. Let’s explore these technologies and understand how they have transformed the world of computing.
Image: www.quora.com
From virtual machines to cloud computing, VT-x and VT-d play a crucial role in the way we access and utilize computing resources. These technologies have essentially revolutionized how we think about and interact with hardware, opening doors to new possibilities and capabilities.
Understanding Intel VT-x and VT-d
Intel VT-x: The Genesis of Virtualization
Intel VT-x, the cornerstone of Intel’s virtualization technology, stands for “Virtualization Technology for x86.” It is a hardware-based feature introduced in Intel’s processors, enabling the creation and management of virtual machines (VMs). This technology allows a single physical processor to emulate multiple virtual processors, each capable of running a separate operating system. VT-x acts as a bridge between the virtual environment and the physical hardware, ensuring the seamless operation of VMs within the confines of the host operating system.
Intel VT-d: Extending Virtualization to I/O Devices
While VT-x focuses on virtualizing the CPU, Intel VT-d, or “Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O,” extends this functionality to peripheral devices. This technology allows VMs to access hardware directly, bypassing the host operating system. This approach not only improves performance but also enhances security by isolating devices from the host operating system. VT-d is particularly beneficial in scenarios where VMs need direct access to specific hardware, such as network interfaces or storage devices.
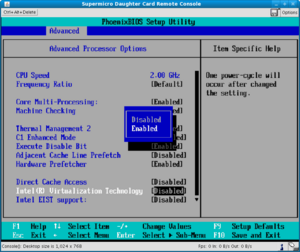
Image: www.thomas-krenn.com
The Impact of VT-x and VT-d
The introduction of Intel VT-x and VT-d has had a profound impact on the computing landscape:
Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
VT-x and VT-d enhance performance by enabling multiple operating systems to share a single CPU and peripheral devices. This eliminates the need for separate physical machines, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency. Virtual machines can run alongside the host operating system without significantly impacting the host’s performance.
Increased Security
By isolating VMs from the host operating system and each other, VT-x and VT-d enhance security. This isolation prevents malicious software running in one VM from compromising other VMs or the host operating system. This is particularly important in environments with sensitive data or numerous users.
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
VT-x and VT-d provide flexibility by allowing users to run different operating systems on a single machine. This allows organizations to easily test different software versions, run legacy applications, or deploy specialized applications without impacting the host operating system. This flexibility also extends to scalability, as users can create and manage multiple VMs as needed, without the need for additional physical hardware.
The Rise of Cloud Computing
The development of virtualization technologies like VT-x and VT-d paved the way for the explosion of cloud computing. These technologies allow cloud providers to create and manage large-scale virtualized environments, offering access to computing resources on demand, without the constraints of physical servers.
Current Trends and Developments
The world of virtualization is constantly evolving, with Intel continually refining and expanding its VT-x and VT-d technologies. Recent developments include:
Improved Performance Optimization
Intel has been actively working on optimizing VT-x and VT-d to further improve performance. This includes incorporating advanced performance features within the technologies, as well as ensuring compatibility with newer processor designs. These advancements are crucial for handling increasingly demanding virtualized workloads.
Enhanced Security Features
Security is always a top priority, and Intel continues to enhance the security features within VT-x and VT-d. New features are being developed to mitigate security threats, such as memory isolation and secure boot technologies, ensuring a secure and trustworthy environment for VMs.
Expanding Virtualization Capabilities
Beyond traditional VMs, Intel is exploring new ways to apply VT-x and VT-d to broader scenarios. This includes supporting newer virtualization technologies like containerization and edge computing. These developments will further expand the range of applications utilizing Intel’s virtualization capabilities.
Tips and Expert Advice
Here’s a few tips based on my experience working with VT-x and VT-d:
Verify Compatibility
Before diving into virtualization, check if your CPU supports VT-x and VT-d. You can find this information in the motherboard’s specifications or by using system information tools like CPU-Z. Ensure that your motherboard’s BIOS is up to date, as this may be necessary for proper virtualization support.
Optimize Virtual Machine Resources
When setting up VMs, allocate sufficient resources, particularly CPU cores and RAM, to ensure optimal performance. This is especially important for resource-intensive applications or VMs running multiple operating systems. Properly managing resources can significantly impact the performance and stability of your VMs.
Consider Security Best Practices
Since VMs are isolated from the host operating system, it’s important to implement security best practices to mitigate security risks. Enable strong passwords and security measures, such as antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect both the host operating system and your VMs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some of the commonly asked questions related to VT-x and VT-d:
Q: What is the difference between VT-x and VT-d?
A: VT-x primarily focuses on virtualizing the CPU, enabling the creation and management of VMs. VT-d extends this functionality to peripheral devices, allowing VMs to access hardware directly, improving performance and security.
Q: Do I need VT-x and VT-d to run virtual machines?
A: While VT-x and VT-d significantly enhance virtualization performance and security, they are not strictly required to run VMs. Software-based virtualization solutions can run on CPUs that don’t support these features. However, performance will be significantly less compared to hardware-based virtualization.
Q: How can I enable VT-x and VT-d on my computer?
A: You can enable VT-x and VT-d in your computer’s BIOS settings. The specific options may vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer. Typically, you can find these options under “Advanced” or “Security” settings.
Q: What are the benefits of using VT-x and VT-d?
A: VT-x and VT-d provide several benefits, including improved performance, enhanced security, increased flexibility, and scalability. They have become integral to modern virtualization technologies, powering cloud computing and a wide range of computing applications.
Intel Vtx And Vtd
Conclusion
Intel VT-x and VT-d are essential components of modern computing, revolutionizing how we manage and utilize computing resources. From enabling powerful virtual machines to driving the growth of cloud computing, these technologies continue to shape the landscape of the tech world. Understanding and harnessing the capabilities of VT-x and VT-d is crucial for anyone looking to maximize the potential of their computing environment.
Are you interested in exploring these technologies further? Do you have any questions about Intel VT-x and VT-d? Let me know in the comments below!






