The world of music production is a playground of sonic possibilities, and there’s no shortage of tools to help artists shape their sound. Among these tools are two prominent techniques that have captured the imagination of producers, engineers, and audiences alike: the talk box and the vocoder. Both techniques offer unique ways to manipulate sound, but they achieve their results through vastly different methods, creating distinctive sonic landscapes.

Image: www.bhphotovideo.com
I first became fascinated with the talk box after hearing the signature sound of Peter Frampton’s “Talk Talk,” a truly innovative musical moment. I was hooked! The humanized, yet otherworldly, sound instantly transported me to another dimension. This was before I even knew what a vocoder was, but as I delved deeper into the world of music production, I discovered a whole universe of sound shaping options that both complemented and contrasted with the talk box. This led me to investigate the world of the vocoder, a technique that, as I soon discovered, held just as much power and potential for sonic creativity.
Dissecting the Difference: Talk Box vs Vocoder
The talk box and vocoder, while both capable of producing a human-like vocal effect, operate on vastly different principles. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating the unique potential of each technique.
The Talk Box: A Mouthpiece for Your Instrument
The talk box is a surprisingly simple device, relying on a combination of a flexible tube and a speaker to create its signature sound. In essence, the talk box utilizes the human mouth as a resonant chamber to alter the sound coming from an instrument.
A musician playing an instrument, typically a guitar or keyboard, connects the instrument’s signal to the talk box. The signal then travels through a speaker within the device and into a flexible tube, which the musician places in their mouth.
By manipulating the shape of their mouth, they shape the sound of the instrument, effectively talking through it.
The Vocoder: Synthesizing Vocals From An Instrument
The vocoder operates from a different sonic plane, leveraging signal processing to achieve its results. In contrast to the talk box, the vocoder essentially analyzes a carrier signal, usually an audio signal from an instrument, and overlays it with information from a modulator signal, typically a vocal track.
Through digital or analog processing, it extracts the frequency information from the modulator and applies it to the carrier, creating a synthesized vocal sound that carries the tonal characteristics of the instrument.
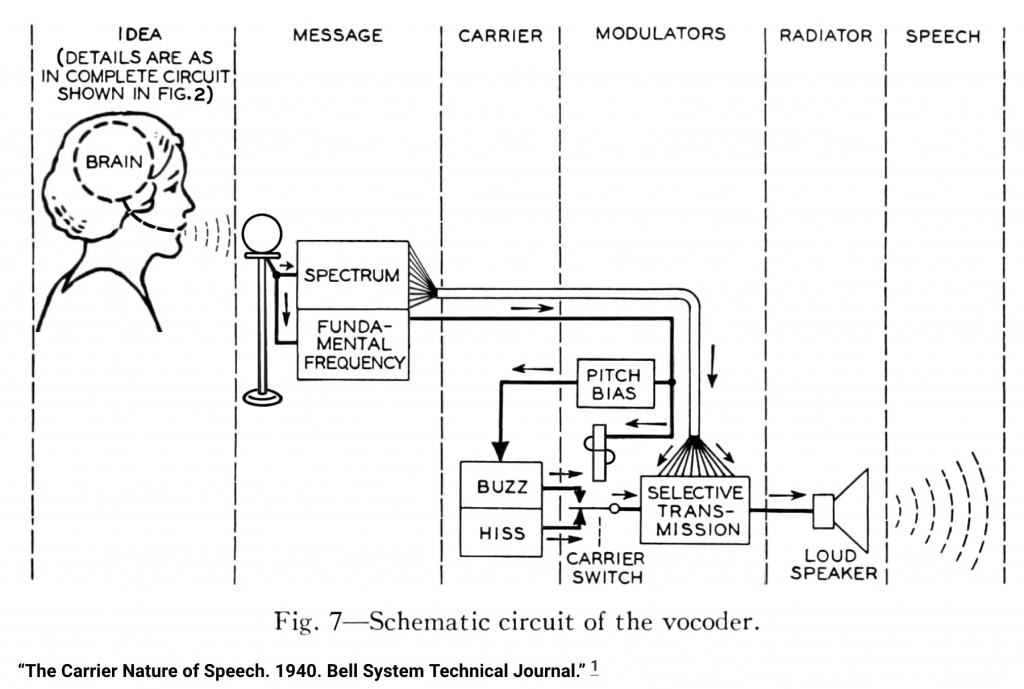
Image: theproaudiofiles.com
From the Analog Era to Modern Software: A Journey of Innovation
The talk box traces its roots to the 1960s, with its earliest iterations used to create distinctive vocal sounds for rock and roll bands. The invention is attributed to Thomas Oberheim, who later honed his audio innovations to create the beloved Oberheim synthesizers. The early talk boxes were often DIY creations, with musicians using vacuum cleaner hoses, and even rubber tubing to create their desired sounds.
Over time, the talk box found its way to the forefront of popular music, with artists such as Peter Frampton, Bon Jovi, and Daft Punk, all using it to create signature effects.
The vocoder also emerged in the late 1960s, first developed by engineers at Bell Labs. Ironically, the vocoder was originally created for communication purposes, making it possible to transmit audio signals over long distances.
Its popularity in music started with the rise of electronic music, with artists like Kraftwerk and Stevie Wonder using it to create synthesized voices and innovative soundscapes. It found its way into the rock world, too, with iconic artists like Herbie Hancock and Parliament playing with its vocal capabilities. As technology advanced, the vocoder’s accessibility grew, making it a mainstay tool for musicians working in a wide range of genres.
Exploring the Pros and Cons: Talk Box vs Vocoder
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technique is crucial for making informed decisions in music production. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of both the talk box and the vocoder:
Talk Box:
-
Pros:
- Authentic Vocal Tone: The talk box offers a uniquely expressive and organic voice effect due to the natural articulation of the human mouth.
- Versatility: Beyond typical vocal effects, it can create a wide range of sounds, from robotic voices to distorted instrument tones.
- Affordable: Talk boxes are relatively inexpensive and easy to find, making them accessible to a broad range of musicians.
-
Cons:
- Limited Control: The sound of the talk box is highly dependent on the user’s ability to manipulate their mouth, which can be challenging to master and require practice.
- Physical Constraints: The need for a flexible tube and the mouth creates a limitation in terms of stage performance and practicality.
- Difficult to Use Live: Due to the mouth placement and instrument signal flow, live performances often require a dedicated engineer or setup.
Vocoder:
-
Pros:
- Precise Control: Vocoders offer a high level of control over the synthesized vocal effect, making it possible to craft nuanced and precise sounds.
- Highly Processable: The vocoder signal can be manipulated further with effects like delay, reverb, and distortion, expanding its creative possibilities.
- Wide Range of Applications: Vocoders are used across a wide range of genres, from electronic music to pop, rock, and even hip hop.
-
Cons:
- Artificial Sound: Although capable of replicating human vocal tones, the vocoder’s synthesized nature often creates a distinctly artificial sound.
- Complexity: The setup and operation of a vocoder, particularly older analog models, can be complex and require a greater level of technical knowledge.
- Limited Vocal Nuance: Compared to the talk box, the vocoder’s vocal characteristics tend to be less expressive and nuanced.
Talk Box and Vocoder in the Digital Age: A New Era of Sound Design
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized the way both the talk box and the vocoder are used in music production.
In the digital realm, both have become accessible to a wider range of musicians, with software emulators and VST plugins offering realistic and versatile recreations of these iconic effects.
Digital plug-ins allow musicians to experiment with different talk box and vocoder settings without the complexities of hardware, making these tools more accessible and user-friendly than ever before.
New digital innovations have also introduced new possibilities for both tools.
Some software recreations of the talk box offer features such as real-time pitch correction and automatic voicing, providing additional control and creative avenues for sound design.
Likewise, digital vocoders have incorporated advanced features like formant shaping, noise reduction, and multi-band processing, offering fine-tuned control over the synthesized vocal effect.
These advancements blur the lines between traditional hardware and digital emulation, creating a playground of sonic possibilities for artists of all levels.
Expert Tips for Mastering the Talk Box and Vocoder
Mastering the talk box and vocoder takes practice and experimentation, but these tips can help you navigate these powerful tools with confidence:
Talk Box:
* Start Simple: Begin by experiment with basic vocal sounds and practice shaping your mouth to create different tones.
* Choose the Right Instrument: Certain instruments like guitar and keyboards lend themselves better to the talk box effect due to their frequency range and tonal characteristics.
* Find the Sweet Spot: Experiment with different mouth positions and microphone placement to discover the ideal balance between articulation and clarity.
Vocoder:
* Choose the Right Carrier: The carrier signal plays a crucial role in defining the overall tone of the vocoded sound. Experiment with different instruments and sounds to find the perfect base.
* Craft the Modulator: The modulator signal provides the vocal information. Experiment with different vocal recordings, processing techniques, and even instrumental samples.
* Fine-Tune the Parameters: Vocoders offer a variety of settings, like formant shaping, carrier/modulator balance, and processing effects. Experiment with different combinations to shape your sound.
FAQs: Talk Box vs Vocoder
Q: What is the difference between a talk box and a vocoder?
A: The talk box uses your mouth as a resonant chamber to shape the sound of an instrument. The vocoder, on the other hand, uses digital or analog processing to analyze a carrier signal and overlay it with a modulator signal to create a synthesized vocal sound.
Q: Which is better, a talk box or a vocoder?
A: There’s no “better” option as both offer unique sounds and creative potential. The choice depends on the desired effect, musical style, and technical preferences.
Q: Can I use both a talk box and a vocoder simultaneously?
A: Yes! Combining techniques like this is a common practice among producers and artists, offering even more sonic possibilities. Experiment with layering these unique sounds to achieve distinctive and innovative musical results.
Talk Box Vs Vocoder
Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of Sound Design
The talk box and vocoder are two powerful sound design tools that have shaped the sonic landscape of music for generations. Whether you’re a seasoned producer or a budding musician, understanding the unique strengths and capabilities of these iconic techniques is crucial for expanding your creative potential.
Explore the world of talk boxes and vocoders, experiment with different techniques, and let your imagination guide you.
The possibilities are endless, and the sounds waiting to be discovered are only limited by your own creativity.
Are you interested in learning more about the talk box or vocoder?
Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!






