Ever found yourself staring at a Bozeman Science video, determined to understand the fundamentals of life, but then hitting a wall of questions? You’re not alone! The engaging style of Bozeman Science videos makes them a popular resource, but sometimes, understanding the intricacies of topics like the molecules of life can be tricky. Whether you’re a student struggling with a concept or an educator looking for answers to guide your lesson plans, this article is here to help.
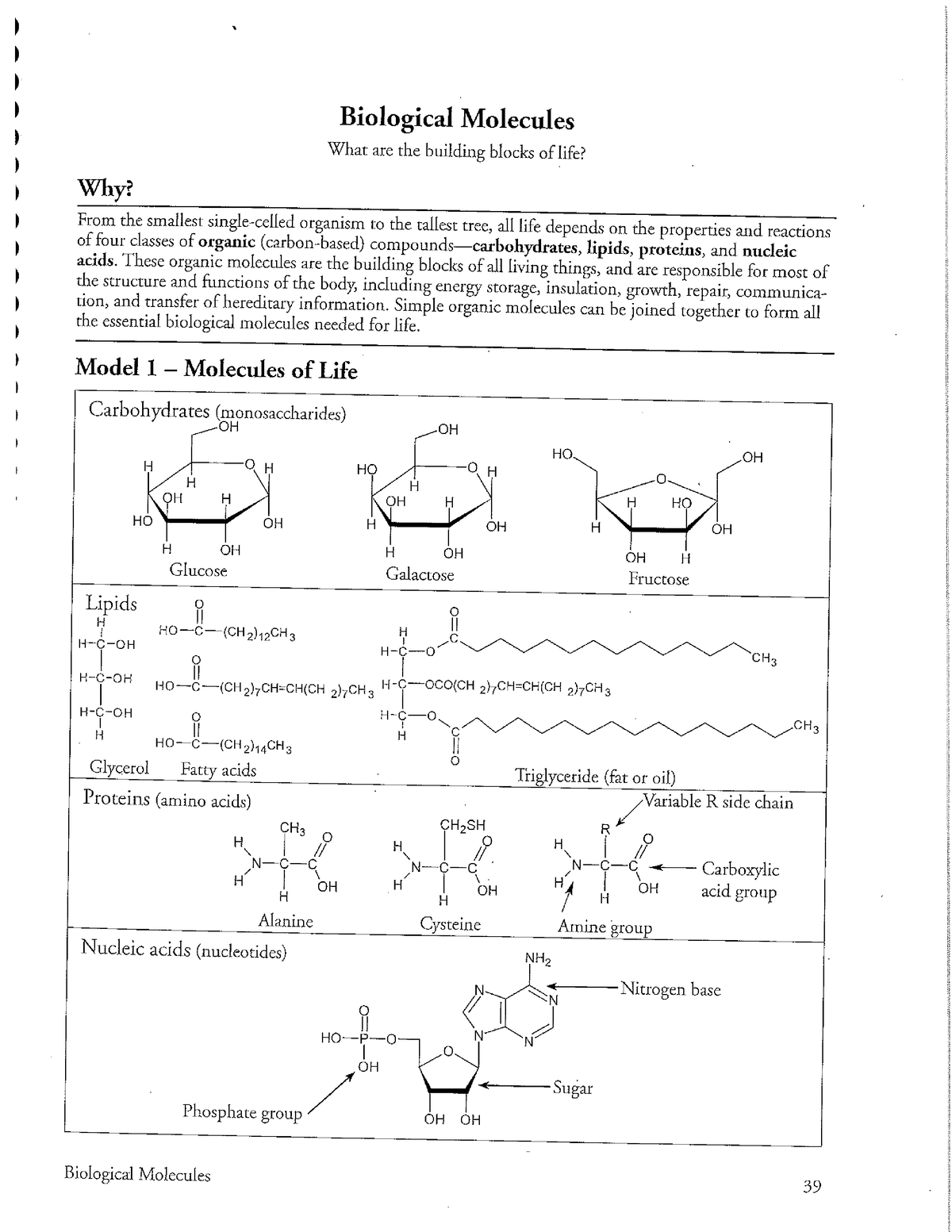
Image: www.studocu.com
I remember struggling with the concept of macromolecules in high school biology. The jumble of monomers and polymers felt like an impenetrable code. It wasn’t until I stumbled upon a Bozeman Science video on the molecules of life, and then spent hours pouring over my notes and quizzes, that those concepts finally started to truly make sense. In this article, I’m going to break down the fundamental molecules of life, addressing common questions and providing insights to help you navigate the world of biology more confidently.
Decoding The Molecules of Life
The very foundation of life, as we know it, rests on the four essential macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These are not just random compounds floating around; they form the building blocks of cells, tissues, and ultimately, entire organisms.
Think of these macromolecules as a team: each molecule has a specific role to play – carbohydrates provide energy, lipids store energy and form important structures, proteins carry out a diverse array of functions (from acting as enzymes to building muscle), and nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
Carbohydrates: Fueling Your Body
Carbohydrates, often referred to as “sugars” or “saccharides,” are the primary energy source for living organisms. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a specific ratio. The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, which are single sugar units. Two monosaccharides linked together form a disaccharide, such as sucrose (table sugar). Longer chains of monosaccharides, like starch and glycogen, are called polysaccharides, and these serve as energy storage molecules in plants and animals, respectively.
Lipids: The Building Blocks of Membranes
Lipids, commonly known as fats, are a diverse group of molecules that are generally insoluble in water. Their structure is characterized by long chains of hydrocarbons (carbon and hydrogen). Lipids include triglycerides (fats and oils) which serve as energy reserves, phospholipids, which make up cell membranes, and steroids, which play vital roles in regulating various bodily functions.
Image: chessmuseum.org
Proteins: The Workhorses of the Cell
Proteins are incredibly versatile molecules that carry out a wide variety of functions in living organisms. They are made up of long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. The sequence and arrangement of these amino acids determine a protein’s unique three-dimensional structure, which in turn dictates its function. Proteins act as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, provide structural support, transport materials, and even defend the body against disease.
Nucleic Acids: The Blueprints of Life
Nucleic acids are the molecules that store and transmit genetic information. There are two main forms: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries the genetic instructions for building and maintaining an organism, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, translating the genetic code into functional proteins.
Understanding the Bozeman Science Video Questions
While Bozeman Science videos provide excellent explanations, the key to truly grasping the concepts lies in actively engaging with the material. Here’s how to use the videos effectively:
1. Watch the Video with a Focused Mind
Before diving into the questions, watch the Bozeman Science video with full attention. Take notes, highlight key points, and pause the video whenever needed for a deeper understanding. Remember, active learning is crucial!
2. Practice with the Bozeman Science Video Questions
After watching the video, use the Bozeman Science video questions as a tool for self-assessment. Try answering the questions without referring back to the video. This will test your comprehension and highlight areas where you need further review.
3. Seek Clarification for Challenging Concepts
If you find yourself stuck on a particular question, don’t get discouraged. Reaccess the portion of the video that covers that concept and take notes on the explanation. If you’re still unclear, seek help from a teacher, tutor, or online forums. There are many resources available to help you understand complex topics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the major types of carbohydrates?
A: The major types of carbohydrates include monosaccharides (single sugar units), disaccharides (two sugar units linked together), and polysaccharides (long chains of sugar units).
Q: What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
A: Saturated fats have all single bonds between their carbon atoms, making them saturated with hydrogen atoms. They are typically solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond between their carbon atoms, which causes them to have fewer hydrogen atoms. They are typically liquid at room temperature.
Q: What are the four levels of protein structure?
A: The four levels of protein structure are primary (the amino acid sequence), secondary (alpha-helices and beta-sheets), tertiary (the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein), and quaternary (the arrangement of multiple protein subunits).
Q: What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
A: DNA is double-stranded, contains the sugar deoxyribose, and uses the base thymine. RNA is single-stranded, contains the sugar ribose, and uses the base uracil instead of thymine.
Bozeman Science Video Questions Molecules Of Life Answer Key
Conclusion: Unlocking the Secrets of Life
Through Bozeman Science video questions, we can delve deeper into the fascinating world of the molecules of life. Understanding these building blocks is essential for grasping the intricacies of biology and appreciating the marvel of life itself. By actively engaging with the videos and seeking clarification when needed, you can confidently answer those Bozeman Science video questions and unlock the secrets of life.
Are you interested in learning more about the molecules of life or the intricacies of Bozeman Science video questions?






