Have you ever wondered why we live in a world of rich and poor, of powerful and powerless? Why do some seem destined for success while others struggle to survive? For Karl Marx, these questions were not simply inquiries into the complexities of human society, but rather the central driving forces behind his sociological thought. Marx, arguably one of history’s most influential thinkers, believed that understanding society requires delving into its very foundations, the intricate web of economic power and social conflict that shapes our lives.
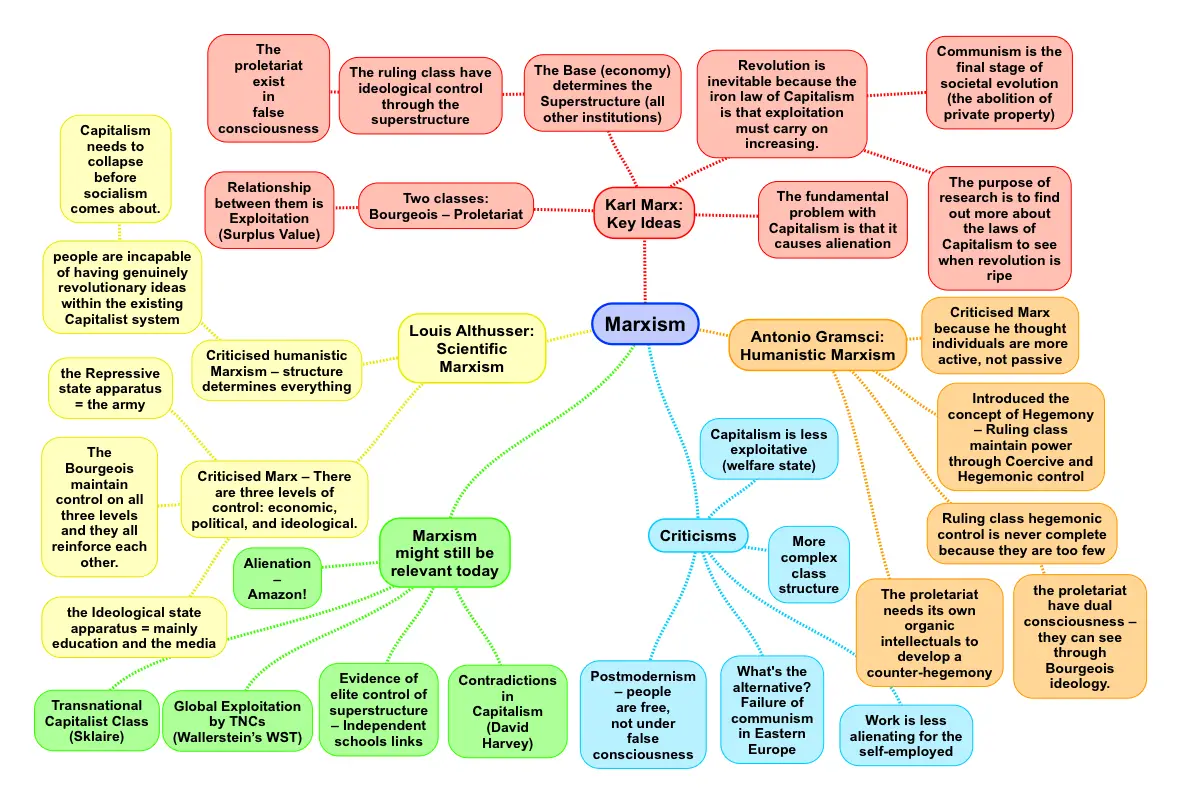
Image: revisesociology.com
This article explores the fascinating and enduring legacy of Karl Marx in sociology. We will delve into his core concepts, particularly his analysis of class struggle, his theories on capitalism and its inherent contradictions, and how these ideas have shaped our understanding of social inequality and revolution. Through a careful exploration of Marx’s work, we aim to shed light on the ever-relevant questions of power, wealth, and the struggles for social justice that continue to shape our world today.
The Seeds of Conflict: Marx’s Theory of Class Struggle
At the heart of Marx’s sociological analysis lies the concept of class struggle. He argued that society is not a harmonious whole, but rather a battleground between opposing forces: the bourgeoisie, the capitalist class who own the means of production (factories, land, etc.), and the proletariat, the working class who must sell their labor to survive. This conflict, according to Marx, is inherent to capitalism, fueled by the fundamental antagonism between those who own and those who work.
Marx saw the bourgeoisie’s pursuit of profit as driving a constant exploitation of the proletariat. He argued that the capitalist system, designed to maximize profit, forces workers to labor for less than the value they create. This “surplus value,” Marx believed, is the source of the bourgeoisie’s wealth and the root of social inequality. This exploitation, in turn, creates a tension between the classes, ultimately leading to a struggle for power and control over the means of production.
The Engine of Change: Capitalism and its Contradictions
Marx’s critique of capitalism goes beyond the simple notion of exploitation. He saw the system itself as inherently flawed, riddled with contradictions that ultimately lead to its demise. These contradictions, he argued, are woven into the very fabric of capitalism, making it a system destined for instability and eventual collapse.
One key contradiction lies in the tendency towards overproduction. In a drive to maximize profits, capitalists constantly seek new markets, pushing for ever-increasing production. However, as production grows, it eventually surpasses the limits of consumption, leading to economic crises and widespread unemployment. This cyclical pattern of boom and bust, according to Marx, demonstrates the inherent instability of capitalism.
Another crucial contradiction lies in the increasing concentration of wealth. As capitalism matures, the gap between the wealthy and the working class widens. This leads to a decline in the purchasing power of the majority, further exacerbating the problem of overproduction. Furthermore, the concentration of wealth also grants the bourgeoisie greater political power, enabling them to shape economic policies in their own interests, further disadvantaging the working class.
The Rise of the Proletariat: Revolution and the End of Capitalism
Marx believed that these contradictions within capitalism, coupled with the growing awareness of their exploitation, would eventually lead to revolution. He saw a future where the proletariat, united by their shared grievances, would rise up to overthrow the capitalist system and establish a classless society – a socialist utopia.
Though Marx’s vision of revolution and a communist future has been debated and challenged throughout history, his ideas have profoundly influenced both sociological theory and political movements. The Marxist perspective, centered on the analysis of class struggle, has been a driving force in movements for social justice and economic equality around the world. From labor rights movements to struggles for racial equality, Marx’s work continues to resonate with those seeking to challenge the existing power structures and achieve a more equitable society.

Image: www.youtube.com
Beyond Revolution: The Enduring Significance of Marx
While Marx’s predictions of imminent socialist revolution have not come to pass in the West, the power of his analysis remains undeniable. His insights into the workings of capitalism, the nature of class struggle, and the inherent contradictions of the economic system continue to be relevant and have shaped much of modern sociology.
In the 21st century, with vast disparities in wealth and income accelerating globally, Marx’s ideas on social inequality and economic exploitation resonate strongly. His work provides a framework for understanding the challenges of globalization, the rise of automation and its impact on labor, and the ever-present tensions between capital and labor.
The study of Marx is not merely about delving into the past or engaging in ideological debate. It is about understanding the intricate forces that shape our modern world, grappling with the complexities of power and inequality, and finding solutions to achieve a more just and equitable society.
Whether one agrees with Marx’s ultimate conclusions or not, his work compels us to think critically about the structures that underpin our society, to question the status quo, and to strive for a world where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
Karl Marx On Sociology
Further Exploration
Marx’s work is vast and complex, offering a wealth of information for those interested in delving deeper. To learn more, consider exploring the following:
- “The Communist Manifesto”: A foundational text outlining Marx and Engles’ vision for a communist society.
- “Capital”: A complex and detailed analysis of capitalism and its internal contradictions.
- The writings of contemporary Marxist theorists: David Harvey, Nancy Fraser, Erik Olin Wright, and others offer insightful analyses of contemporary social issues through a Marxist lens.
The study of Karl Marx is an ongoing journey, one that invites us to engage with the critical questions of power, inequality, and the future of society. As we continue to grapple with the challenges of our time, Marx’s ideas provide us with a valuable framework for understanding our world and seeking a more just and equitable future.






