Walking down the bustling streets of a city, you might encounter a symphony of institutions: towering skyscrapers housing corporations, serene libraries filled with knowledge, and vibrant schools brimming with curiosity. These institutions, each with a distinct purpose and structure, play a vital role in shaping our society and the world around us. The sheer variety of institutions can be overwhelming, but understanding their different types can provide invaluable insights into how our world functions and how we engage with it. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse landscape of institutions, shedding light on their roles, characteristics, and significance.
Image: learningcurveformula.blogspot.com
From the moment we are born, institutions become an integral part of our lives. We are welcomed into the world by a hospital, nurtured in schools, and guided by laws and regulations. Throughout our journeys, we encounter various institutions, each contributing in unique ways to our individual and collective experiences. This guide will delve into the fascinating world of institutions, exploring the diverse range of types and their profound impact on our lives.
The Essence of Institutions
In the realm of social sciences, an institution refers to a structured and enduring set of social practices, rules, and norms that govern the behavior of individuals within a given society. These institutions provide frameworks for order, stability, and continuity, allowing societies to function effectively. Think of them as the underlying infrastructure that supports our daily lives, guiding our actions and shaping our interactions.
For instance, the institution of marriage defines the legal and social framework for romantic relationships, establishing rights and responsibilities for partners. The institution of education provides pathways for knowledge acquisition and skill development, preparing individuals for future roles in society. Institutions can range from formal organizations with clearly defined structures, like government agencies and corporations, to informal social groups that shape our behavior through shared values and traditions, such as family units and religious communities.
Types of Institutions: A Diverse Spectrum
The multifaceted nature of institutions gives rise to a wide spectrum of types, each with its own unique characteristics and functions.
1. Economic Institutions
Economic institutions are responsible for the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services within a society. Examples include:
- Corporations: Legally recognized entities that operate for profit, employing individuals and producing goods or services.
- Banks: Financial institutions that provide financial services, such as loans, deposits, and money transfers.
- Stock Markets: Platforms where investors buy and sell shares in publicly traded companies.
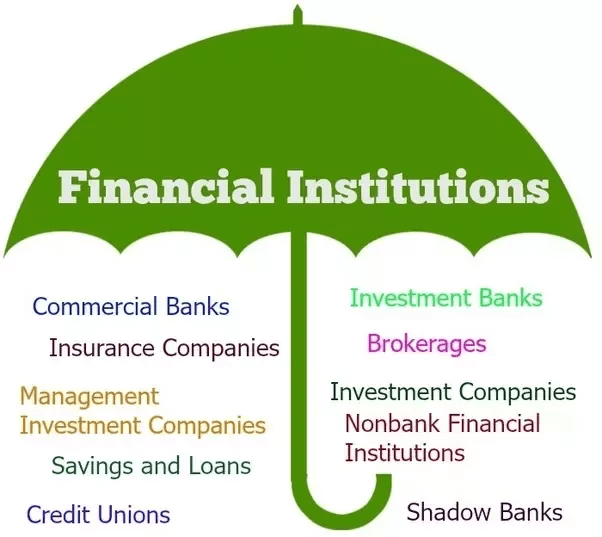
Image: www.javatpoint.com
2. Political Institutions
Political institutions establish the framework for governing a society, determining how power is distributed, laws are made, and conflicts are resolved. Examples include:
- Governments: Organizations responsible for making and enforcing laws, providing public services, and ensuring national security.
- Political Parties: Groups of individuals with shared political ideologies and aims, competing for power within the political system.
- Courts: Judicial bodies that interpret and apply the law, resolving disputes and ensuring justice.
3. Social Institutions
Social institutions are responsible for shaping social norms, providing support systems, and fostering social cohesion. Examples include:
- Family: The basic unit of society, providing care, socialization, and emotional support.
- Education: Institutions that provide structured learning experiences, transmitting knowledge and skills to individuals.
- Religion: Systems of beliefs and practices that provide spiritual guidance, moral principles, and a sense of community.
4. Cultural Institutions
Cultural institutions play a vital role in preserving and disseminating a society’s cultural heritage, arts, and traditions. Examples include:
- Museums: Organizations dedicated to collecting, preserving, and exhibiting artifacts and artworks.
- Libraries: Collections of books and other resources that provide access to information and knowledge.
- Theaters: Performance spaces where art forms such as drama, dance, and music are showcased.
Trends and Developments in Institutions
Institutions are constantly evolving in response to social, economic, and technological changes. Recent trends include:
- Globalization: Increased interconnectedness and interdependence between nations, leading to the rise of global institutions like the United Nations and the World Trade Organization.
- Digital Transformation: The growing influence of digital technologies on institutions, transforming how they operate, communicate, and interact with individuals. This includes the rise of online education platforms, e-commerce businesses, and social media networks.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: Growing demand for greater transparency and accountability from institutions, driven by technological advancements and public awareness of their impact on society.
Tips for Engaging with Institutions
Understanding the different types of institutions is essential for actively engaging with your community and society. Here are some tips:
- Stay informed: Keep up with current events and developments related to institutions, particularly those that impact your life, such as education, healthcare, or the economy.
- Participate in civic engagement: Exercise your right to vote, volunteer in your community, and engage in discussions and debates on important societal issues.
- Support institutions: Contribute to institutions that align with your values, whether through donations, volunteering your time, or advocating for their policies.
By engaging with institutions, you can contribute to shaping a more just, equitable, and sustainable future for yourself and your community.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between an organization and an institution?
An organization is a structured group of people with a specific purpose. Institutions are broader concepts that encompass established patterns of social behavior, rules, and norms. Organizations are examples of institutions, but not all institutions are organizations.
Q: How can institutions be reformed or improved?
Institutional reform can occur through various means, including legislative changes, public pressure, and social movements. It often involves addressing issues of inequality, corruption, and inefficiency within institutions.
Q: What is the role of technology in shaping institutions?
Technology plays a transformative role in shaping institutions, enabling greater efficiency, accessibility, and communication. However, it also raises concerns about privacy, security, and potential for manipulation.
Types Of Institutions
Conclusion
The diverse types of institutions play a pivotal role in shaping our world, providing frameworks for order, stability, and progress. From economic institutions driving economic growth to social institutions building communities, each type contributes in unique ways to our collective experiences. Understanding these institutions, their functions, and their evolving landscape can empower individuals to navigate the complexities of modern society and contribute to a more just, equitable, and sustainable future.
Are you interested in exploring the fascinating world of institutions further? What other types of institutions pique your curiosity?






