Imagine walking into a bustling marketplace, filled with sights, sounds, and a multitude of interactions. You see people haggling over prices, exchanging kind words with friends, and even displaying anger towards someone who cuts the line. This scene, though seemingly mundane, is a microcosm of human society – a tapestry woven with countless values that shape our interactions, beliefs, and behaviors.
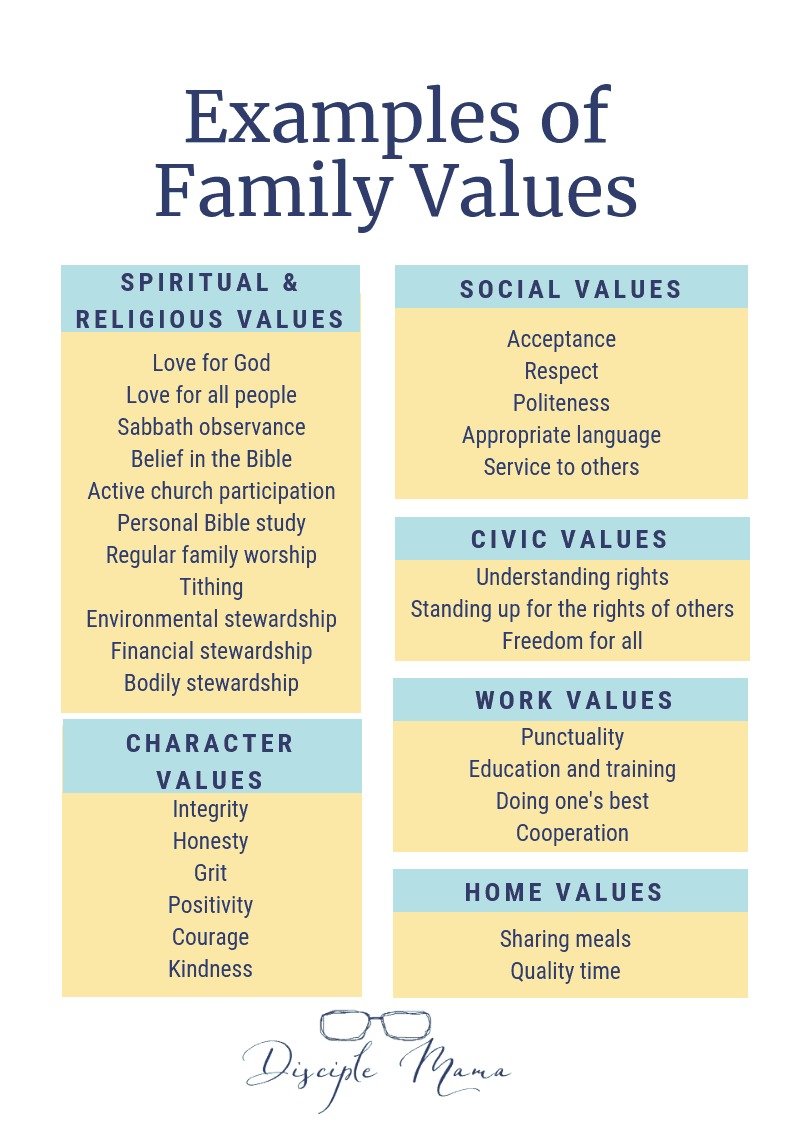
Image: amazonia.fiocruz.br
Sociology, the study of human society, delves deep into understanding these values and their profound impact on our lives. But what exactly are values, and how do they manifest in our daily interactions? From the subtle norms of politeness to the deeply held convictions about justice, values form the bedrock upon which social structures are built. This article will explore these fascinating examples, shedding light on how they influence our individual choices and collective destinies.
A Foundation of Shared Beliefs: The Cornerstone of Society
Values, in the context of sociology, are deeply held beliefs that influence our perceptions, attitudes, and actions. They are the shared moral principles, ideals, and aspirations that guide our behaviors and give meaning to our lives. Think of them as the invisible threads that hold together the fabric of society.
Societies often develop a set of core values that reflect their history, culture, and beliefs. These values are often codified in laws, customs, and traditions. For instance, in many cultures, respect for elders is highly valued, leading to specific forms of address and deference towards older generations.
Examples of Values in Action
Let’s delve deeper into the world of values with some illustrative examples:
1. Individualism vs. Collectivism: A Clash of Priorities
Two fundamental values often clash in our understanding of society: Individualism and collectivism. Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and achieving success through individual effort. This value is often associated with Western societies and is reflected in their emphasis on personal freedoms and achievement.
Collectivism, on the other hand, emphasizes the importance of the group. This value emphasizes cooperation, social harmony, and fulfilling one’s duty towards the collective good. Collectivist societies, often found in many Asian and African cultures, prioritize group cohesion and family loyalty.
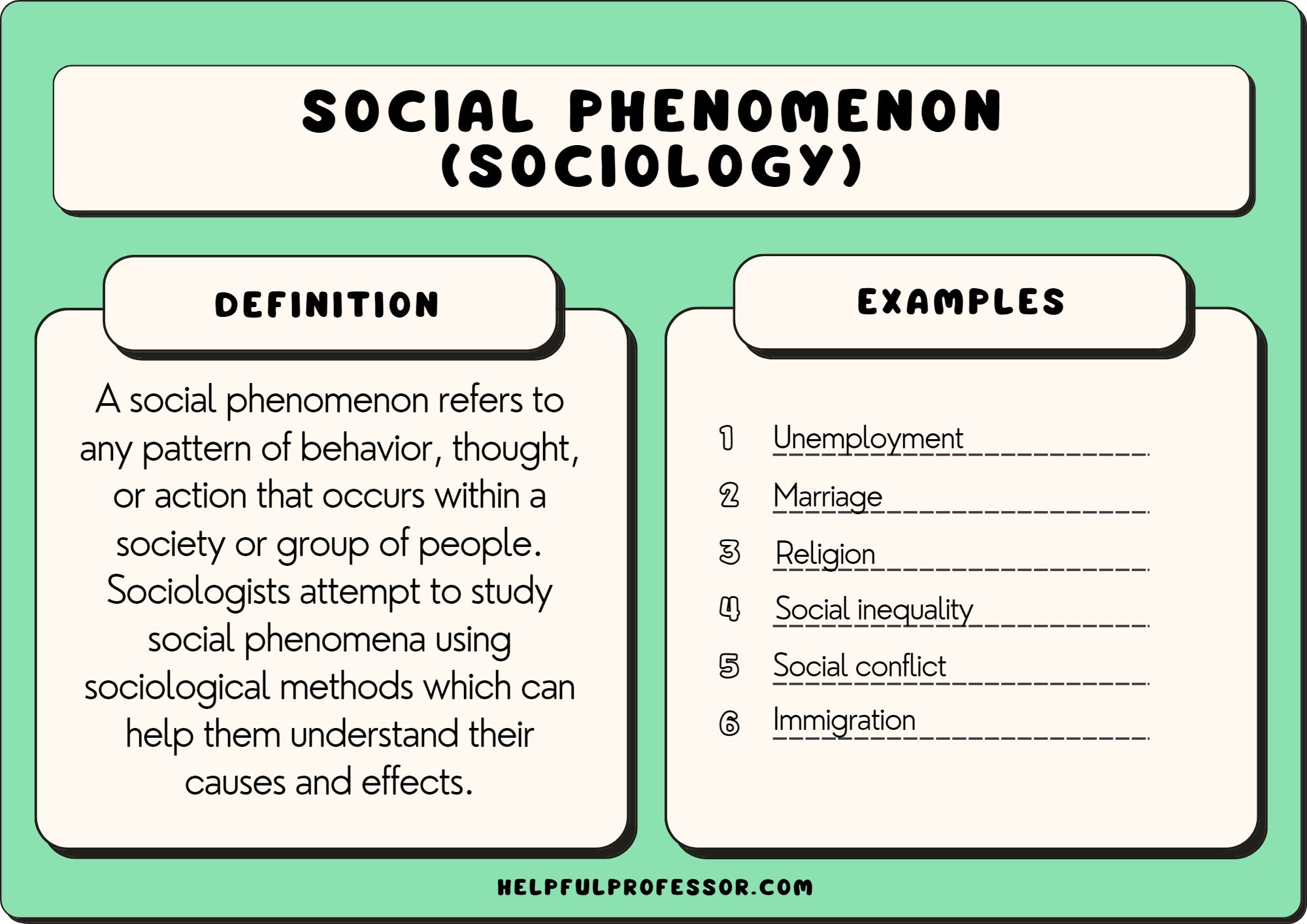
Image: helpfulprofessor.com
2. Equality and Justice: Striving for Fairness
Equality and justice are two values that are deeply entwined and often serve as the bedrock of progressive social movements. Equality emphasizes the principle that all individuals should be treated with equal dignity and respect regardless of their socioeconomic background, race, gender, or sexual orientation. Justice, on the other hand, focuses on ensuring fairness and holding individuals accountable for their actions.
These values have historically fueled social justice movements like the fight for civil rights, LGBTQ+ rights, and women’s suffrage.
3. Materialism vs. Sustainability: Balancing Progress and Preservation
In today’s world, we are confronted with a stark choice between materialism and environmental sustainability. Materialism places a high value on acquiring material possessions, financial wealth, and consumerism. It often drives economic growth but can also lead to unsustainable consumption patterns and environmental degradation.
Sustainability, on the other hand, emphasizes responsible use of resources, ecological balance, and long-term well-being for both present and future generations. It recognizes the interconnectedness between human society and the environment, advocating for mindful consumption and responsible stewardship of our planet.
4. Truth and Transparency: Foundations of Trust
Trust is a vital component of any functional society. Truth and transparency are fundamental values that lay the groundwork for trust. Truthfulness emphasizes honesty and accuracy in communication, while transparency fosters open and accountable governance.
These values are crucial for maintaining public confidence in institutions, ensuring fair and ethical behavior among individuals, and promoting informed decision-making.
5. Compassion and Empathy: Building Bridges of Understanding
Compassion and empathy are essential values that foster understanding and kindness. They encourage individuals to recognize the suffering of others, extend a helping hand, and build bridges of mutual support.
Compassion motivates us to act for the well-being of others, while empathy enables us to step into their shoes and understand their perspectives. These values are invaluable for creating a more humane and compassionate world.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
Sociologists like Dr. Alice Eagly, a leading expert in the field of gender and social psychology, emphasize the importance of critically examining our own values and understanding how they mold our interactions with the world. Dr. Eagly suggests actively questioning our biases, seeking diverse perspectives, and engaging in open dialogue to challenge our assumptions.
We can all leverage these insights in our lives by:
- Being mindful of our own biases: Pay attention to our reactions and thoughts, especially in situations where we encounter people from diverse backgrounds.
- Seek out diverse perspectives: Engage with people who hold different viewpoints and actively listen to their experiences.
- Engage in respectful dialogue: Focus on constructive conversations, actively seeking common ground and finding ways to bridge differences.
Examples Of Values In Sociology
Conclusion
From the bustling marketplace to the quiet corners of our minds, values are the driving forces behind our interactions and choices. They shape our social structures, guide our actions, and define our individual and collective identities. By delving into the diverse examples of values in sociology, we gain a deeper understanding of the tapestry of human interaction and the complex forces that shape our world.
This journey of exploration is ongoing, and we can all contribute to a more just and compassionate society by critically examining our values, embracing diversity, and engaging in constructive dialogue.






