Imagine walking into a party and being surrounded by people who seem to effortlessly glide through social interactions, their words carrying weight and their opinions influencing others. You, on the other hand, feel awkward, lost in a sea of connections you don’t quite understand. This feeling speaks to the powerful, yet often unacknowledged, force of status in our lives. We all navigate a complex web of social hierarchies, even if we don’t always recognize it. In the realm of sociology, status is a fascinating concept that unravels the dynamics of power, influence, and identity that shape our experiences. Through the lens of sociology, we gain a deeper understanding of how status operates, influencing our opportunities, relationships, and even our self-perception.
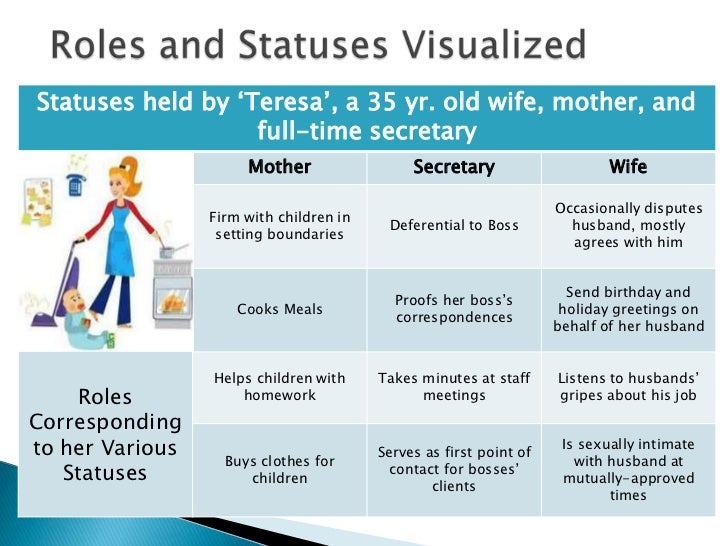
Image: articlelawphil.web.fc2.com
Sociology Status Examples delve into the intricate ways in which individuals and groups are ranked within society. These rankings are not merely based on wealth or fame, but rather encompass a spectrum of factors such as education, occupation, social networks, and even our perceived cultural capital. By examining these examples, we can unlock a deeper understanding of the unseen forces that shape our interactions and behaviors. It’s not just about understanding how others perceive us, but also how our own perception of status can affect our choices and opportunities.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Status
The concept of status within sociology is multifaceted, drawing on insights from different theoretical perspectives. It’s crucial to grasp the various dimensions of status to truly comprehend its impact on our lives.
Ascribed Status vs Achieved Status
One fundamental distinction lies between ascribed status and achieved status. Ascribed status refers to positions we are born into, largely determined by factors like family background, ethnicity, or race. For example, being born into a wealthy family or belonging to a particular cultural group can confer certain social advantages. On the other hand, achieved status is gained through effort, talent, and our choices. This can include pursuing higher education, building a successful career, or attaining recognition for our contributions. While ascribed status can offer a starting point, it’s often achieved status that shapes our individual trajectories.
Status Sets and Master Status
Our lives are not defined by a single status, but rather a complex interplay of multiple statuses. Sociologists refer to this as a status set, which encompasses our various social positions and roles. For instance, you might be a student, a friend, a child, a volunteer, and an employee, all at the same time. Each of these statuses carries its own associated expectations and behaviors. However, within this set, a master status often emerges as the most dominant, overshadowing other aspects of our identity. For some, it might be their profession, while for others, it might be their disability, ethnicity, or even their social activism.

Image: study.com
Status Symbols and Consumption Patterns
Status is not always explicit, but often communicated through status symbols. These are material possessions, behaviors, or affiliations that signal a particular social position. A luxury car, a high-end handbag, or even a specific type of clothing can act as status symbols, indicating wealth, taste, or a particular social group. This is closely linked to conspicuous consumption, a concept introduced by sociologist Thorstein Veblen, which describes the ostentatious display of wealth and status through consumption patterns.
Status and Social Stratification
Status plays a crucial role in understanding social stratification, the hierarchical arrangement of individuals and groups within society. These hierarchies are built upon various factors like income, education, occupation, and social capital. Sociologists utilize concepts like social class, socioeconomic status, and social mobility to map these hierarchies and explore their impact on individual and collective opportunities.
Exploring Sociology Status Examples in Action
To fully grasp the influence of status, let’s explore some compelling real-world examples:
The Power of Education: A Status Symbol
Imagine two individuals applying for the same job. One has a high school diploma while the other holds a doctorate degree. In many contexts, the doctor’s degree acts as a potent status symbol, signaling a higher level of knowledge and expertise. This often translates into advantages in employment opportunities, salaries, and access to networks. However, it’s important to recognize that education, as a status symbol, can be influenced by historical and social factors, such as access to quality education and systemic biases.
The Influence of Occupation: A Status Hierarchy
We frequently encounter the impact of status when it comes to occupations. A physician, for instance, holds a high-status position due to their specialized knowledge, extensive training, and ability to deliver essential medical care. This perceived status often translates into respect, influence, and even financial rewards. Conversely, occupations like janitors or retail workers might be perceived as lower-status jobs, even though they are equally vital to societal functioning.
Social Networks and Status: Who You Know Matters
The power of social networks to influence status cannot be underestimated. The connections we cultivate can open doors to opportunities, provide support, and shape our social standing. For instance, belonging to an exclusive club, being part of a prestigious alumni network, or being friends with influential individuals can confer status and provide access to resources that might otherwise be unavailable. However, it’s important to be wary of social networks that reinforce existing inequalities or exclude diverse perspectives.
Gender and Status: Navigating Societal Expectations
Gender remains a potent force in shaping status. Societal expectations around roles, behaviors, and opportunities often differ for men and women. For example, women in leadership positions, while making strides, still face the “glass ceiling” effect, where they encounter barriers to advancement despite achieving similar levels of competence and qualifications as their male counterparts.
Racial and Ethnic Status: The Impact of Social Structures
Race and ethnicity have traditionally been deeply intertwined with social status. While strides are being made in dismantling systemic racism and discrimination, historical inequalities and prejudices continue to shape opportunities, privilege, and social mobility. For instance, individuals from minority racial groups often face challenges gaining access to education, employment, and housing, despite their talents and qualifications.
Digital Status and Social Media
The rise of social media has introduced a new dimension to status, shaping a complex interplay between online presence and social standing. Influencers, bloggers, and online personalities wield significant influence, often using their platforms to build brands, promote products, and shape trends. The number of followers, likes, and shares can act as digital status symbols, influencing perceptions and garnering attention. However, it’s important to be mindful of the potential for online bullying, misinformation, and the pursuit of validation, which can negatively impact mental well-being.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
To navigate the complexities of status in a socially conscious manner, experts recommend:
- Cultivating Self-Awareness: Be acutely aware of how your own perceptions of status might influence your interactions and opportunities. Challenge your assumptions and consider how your status might advantage or disadvantage others.
- Embracing Diversity and Inclusivity: Promote equity and inclusion in all social settings. Recognize and challenge the status quo that might perpetuate discrimination and bias based on factors like race, gender, sexual orientation, or disability.
- Focus on Contribution: Instead of striving for prestigious titles, focus on contributing your skills and passions to a greater purpose. True value lies in making a positive impact, regardless of your social standing.
Sociology Status Examples
Conclusion
Exploring sociology status examples offers a powerful lens through which to analyze the complex and often unspoken dynamics of power, influence, and identity within society. By understanding the various concepts and examples, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shape our lives. When we become more self-aware of the role status plays in our interactions and choices, we can make more informed decisions that promote equity, empathy, and positive social change. Let’s work together to create a society where status is not based on privilege but on the value we bring to the world and the contributions we make to the collective good.






