Have you ever stopped to consider the forces that shape our lives? The way we interact with each other, the institutions we build, and the beliefs we hold – are these simply products of individual choices, or are there larger, often invisible, structures at play? This is where sociology steps into the spotlight, offering us a lens through which to understand the intricate tapestry of human society.

Image: blog.bintangasik.com
Sociology, the scientific study of human society and social behavior, plays an instrumental role in unraveling the complexities of our world. It equips us with the tools to analyze social phenomena, understand the dynamics of power and inequality, and ultimately, contribute to creating a more equitable and just society.
Unearthing the Foundations: History and Key Concepts
From Early Observations to Systematic Study
The seeds of sociology were sown long before the formal establishment of the discipline. Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle pondered the nature of society and the role of the individual within it. However, it was in the 18th and 19th centuries, amidst profound societal changes fueled by industrialization and urbanization, that sociology emerged as a distinct field of study. This period witnessed the rise of thinkers like Auguste Comte, who coined the term “sociology” and emphasized the importance of applying scientific methods to understand social phenomena.
The Building Blocks of Social Analysis
Sociology relies on a set of fundamental concepts that provide the framework for analysis:
- Social Structure: The underlying patterns of social relationships that organize society. Think of it as the scaffolding that holds society together, influencing our interactions and shaping our experiences.
- Culture: The shared beliefs, values, norms, and practices that characterize a group of people. It’s what defines our customs, traditions, and ways of life.
- Socialization: The process by which we learn the norms, values, and behaviors of our society. It’s how we become members of the social world and internalize its rules.
- Social Institutions: Stable and enduring patterns of social behaviour that organize our lives and meet our needs. Examples include family, education, religion, and government.
- Social Inequality: Uneven distribution of resources, power, and privileges within a society. It manifests in various forms, such as economic disparity, racial discrimination, and gender bias.
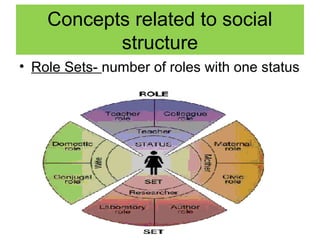
Image: www.slideshare.net
Exploring the Impact: Applications of Sociology in the Real World
Sociology is not merely an academic pursuit; it has concrete applications across various fields and influences our daily lives in numerous ways.
Understanding Social Issues: A Window into Complexities
Sociologists play a vital role in illuminating the root causes and consequences of social issues like poverty, crime, and health disparities. By analyzing the social structures, cultural factors, and historical contexts, they provide insights into the complex interplay of forces shaping these issues, helping us develop more effective solutions.
For example, a sociologist studying poverty might examine the relationship between socioeconomic inequality, access to education, and employment opportunities. They might investigate the impact of discriminatory policies or the influence of cultural factors on poverty rates.
Shaping Public Policy: Informing Decision-Making
Sociological research provides empirical evidence that helps inform public policy decisions. By analyzing data on social trends, demographics, and public attitudes, sociologists contribute to policy development in areas such as education, healthcare, and social welfare.
For instance, sociological research on the effectiveness of different educational programs can inform policy decisions to improve student outcomes. Similarly, sociological data on the impact of government policies on marginalized groups can help policymakers address inequalities.
Enhancing Communication and Understanding: Bridging the Divide
Sociology helps us understand diverse perspectives and cultural values, fostering empathy and promoting intercultural communication. It encourages us to analyze our own biases and assumptions, leading to greater understanding and tolerance of other cultures and ways of life.
Fueling Social Change: Empowered Individuals, Empowered Societies
Sociology is not just about understanding society; it’s also about actively contributing to its improvement. By exposing inequalities and challenging social norms, sociology empowers individuals to advocate for change and create a more just and equitable society.
For example, sociological studies on gender inequality have contributed to movements advocating for women’s rights, equal pay, and representation in leadership positions.
Current Trends and Future Directions
Sociology is a dynamic field constantly evolving to address the changing complexities of our world. Here are some of the current trends and future directions:
The Rise of Digital Sociology
With the increasing impact of technology on social interactions, digital sociology examines the ways social media, online communities, and virtual reality shape our lives, relationships, and perceptions of the world. It explores how technology influences social movements, political discourse, and the spread of misinformation.
Global Sociology
Global sociology transcends national borders, studying the interconnectedness of societies and the impact of globalization on social structures, cultures, and inequalities. It examines issues like international migration, environmental justice, and the rise of transnational corporations.
Environmental Sociology
Amidst growing environmental concerns, environmental sociology investigates the relationship between human societies and the natural environment. It examines the social consequences of climate change, resource depletion, and environmental inequality, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices and social change.
Instrumental Role Sociology
Conclusion: A Vital Lens for a Changing World
Sociology offers us invaluable tools for navigating the complexities of our modern world. By providing insights into the forces that shape our lives, it empowers us to participate in meaningful dialogue, contribute to social change, and build a more just and equitable society. Whether you’re interested in understanding social issues, contributing to public policy, or simply wanting to gain a deeper appreciation of human interactions, sociology holds the key to a richer and more informed understanding of the world around us.
We encourage you to engage with this dynamic field, explore the wealth of sociological research, and contribute to building a society that values diversity, justice, and the well-being of all its members.






