Imagine walking into a bustling party, a symphony of laughter, music, and conversation swirling around you. The air crackles with unspoken tension, flirting, and the thrill of connection. You observe couples dancing, friends sharing secrets, and individuals navigating the intricate landscape of attraction and intimacy. Now, imagine stepping back from this scene and viewing it through a sociological lens. Suddenly, the party transforms into a fascinating tapestry of social interactions, power dynamics, and cultural norms surrounding sexuality.
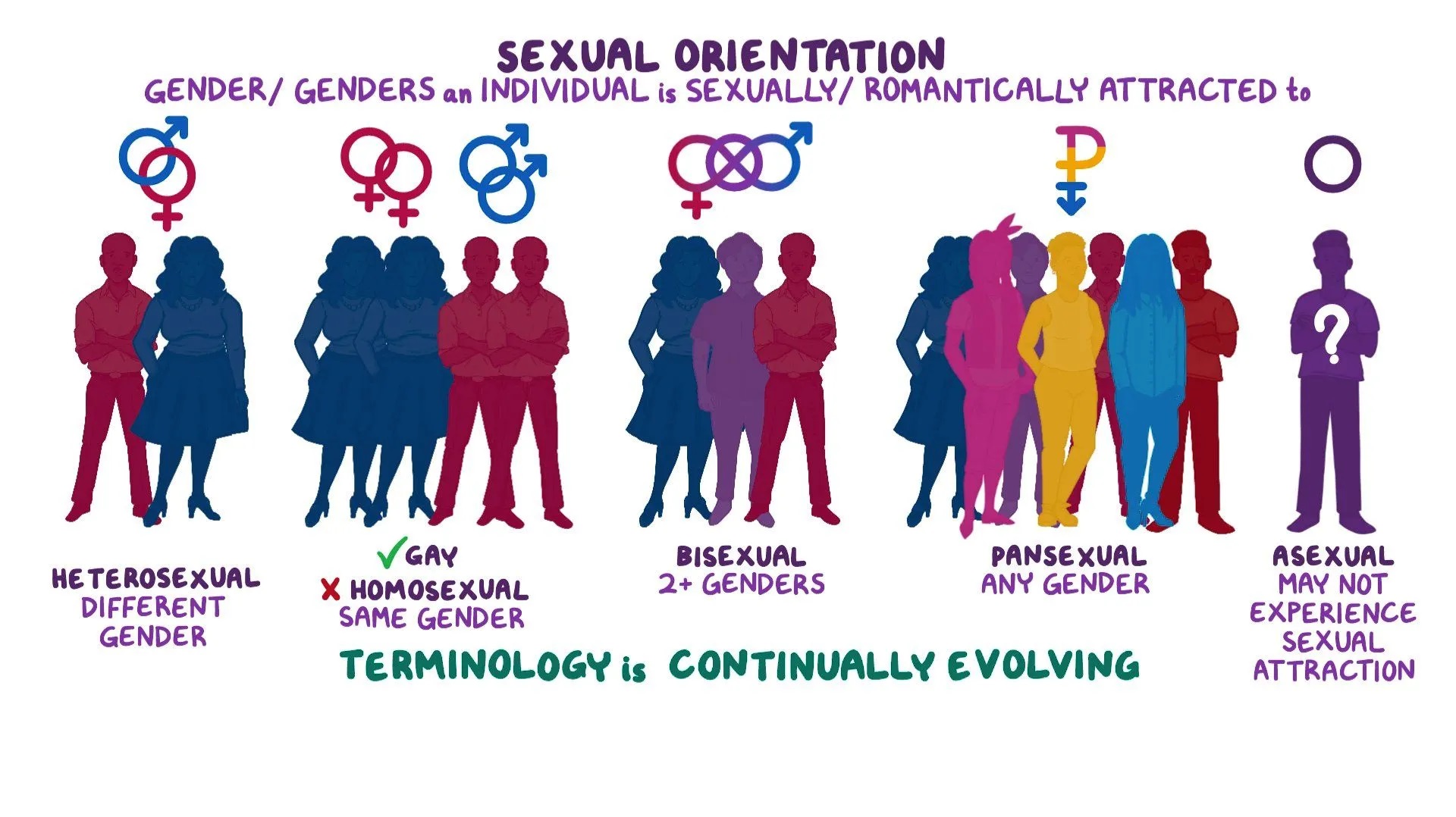
Image: womansera.com
The study of sexuality through a sociological perspective reveals the profound influence of society on our understanding, experiences, and expressions of intimacy. It’s not simply about personal preferences; it’s about the deep-rooted social structures, cultural beliefs, and historical forces that shape our sexual lives. This lens empowers us to see beyond the individual and decipher the societal forces that underpin our most personal desires and choices.
Unveiling the Social Construction of Sexuality: Breaking Free from Predetermined Scripts
One of the most compelling reasons to study sexuality through a sociological lens is to understand the concept of “social construction.” This idea challenges the notion of sexuality as solely an innate, biological drive. Instead, it emphasizes the role of societal influences in shaping our understanding, norms, and expressions of sexuality.
Think about how different cultures perceive and practice sexual expression. In some societies, arranged marriages are the norm, while in others, casual relationships are commonplace. These variations highlight the cultural variations in what is considered acceptable, desirable, and even taboo.
This societal construction of sexuality extends beyond cultural boundaries and permeates various aspects of our lives:
- Gender Roles: Traditional gender roles often influence what types of sexual behavior are deemed appropriate for men and women.
- Race and Ethnicity: Social attitudes and power structures influence sexual experiences and access to resources, creating disparities and inequalities within different racial and ethnic groups.
- Social Class: Socioeconomic factors influence sexual practices, access to sexual health care, and even the language used to discuss sexuality.
- Media and Culture: The portrayal of sexuality in media, literature, and art shapes our understanding of what is considered attractive, desirable, and acceptable.
By analyzing these social forces, we can challenge restrictive norms and develop a more inclusive and nuanced understanding of human sexuality.
Beyond the Individual: The Power of Social Context
The sociological perspective encourages us to move beyond individualistic explanations of sexual behavior and acknowledge the broader social context. For example, consider the phenomenon of sexual harassment. While some may attribute it to individual personality flaws, sociology helps us understand the social systems that allow for such behavior to flourish.
Here are some key sociological dimensions that illuminate the issue of sexual harassment:
- Power dynamics: Often, sexual harassment occurs within power imbalances, where one party holds more authority or influence over the other.
- Social norms: Societies often tolerate or even normalize certain forms of sexual harassment, making it more difficult for victims to speak out.
- Cultural beliefs about masculinity and femininity: Toxic masculinity can perpetuate objectification and aggression towards women, contributing to the prevalence of sexual harassment.
By understanding the broader social context, we can develop more effective strategies to prevent and address sexual harassment.
Navigating the Complex Landscape of Sexuality: A Sociological Toolkit
The study of sexuality through a sociological perspective offers a valuable toolkit for navigating the complexities of modern relationships and sexual practices. It provides us with:
- Critical thinking skills: Sociology equips us with the ability to question taken-for-granted assumptions about sexuality and to consider alternative perspectives.
- Understanding power dynamics: It helps us identify and analyze how power structures influence sexual interactions and relationships.
- Awareness of social inequalities: Sociology shines a light on how social forces create disparities in access to sexual health resources, information, and rights.
- Empowerment to challenge social norms: By understanding how sexuality is socially constructed, we can critically evaluate and challenge restrictive norms, promoting greater freedom and autonomy.

Image: www.studocu.com
Expert Insights on Studying Sexuality through a Sociological Lens
Renowned sociologist Dr. Arlene Stein, author of “Sex and Gender: An Introduction,” emphasizes the importance of studying sexuality in its social context. She states, “Understanding the social forces that shape our sexual lives is crucial to creating a more just and equitable world for all.”
Dr. Stein encourages individuals to actively engaging in critical analysis of their own experiences and interactions. “By questioning the ‘naturalness’ of our own beliefs and practices, we can begin to dismantle harmful stereotypes and create more inclusive spaces for understanding and expressing our sexuality,” she asserts.
Putting Sociology in Action: Transforming Lives and Communities
The insights gained from studying sexuality through a sociological lens have profound implications for various fields:
- Public Health: Sociologists play a vital role in designing and implementing effective sexual health education programs that address the unique needs of diverse communities.
- Social Policy: The understanding of social inequalities in sexual health access informs policies aimed at promoting reproductive rights, preventing sexually transmitted infections, and providing comprehensive sexual health services.
- Education: Integrating sociological perspectives in sex education curricula helps students develop critical thinking skills, challenge harmful stereotypes, and learn about the complexities of sexuality in a respectful and inclusive manner.
- Human Rights: Sociology is an invaluable tool in advocating for LGBTQ+ rights, challenging discriminatory practices, and promoting equality and social justice within the context of sexuality.
A Reason To Study Sexuality Using The Sociological Perspective Is
https://youtube.com/watch?v=kjXfe56fZas
Conclusion
Studying sexuality through a sociological lens offers a profound and empowering understanding of our deepest desires, choices, and experiences. By recognizing the influence of social forces on our understanding of intimacy, we gain the capacity to challenge restrictive norms, dismantle harmful stereotypes, and create more inclusive and equitable societies. So, the next time you find yourself at a party, remember to observe and analyze the social interactions, the power dynamics, and the cultural cues that shape the way we navigate desire, attraction, and connection. By embracing the sociological lens, we can unlock a deeper understanding of ourselves and the world around us.






