Have you ever wondered why your blood is red? It’s a question that has fascinated scientists and curious minds for centuries. The answer, of course, lies in the presence of a remarkable protein called hemoglobin, which gives our blood its characteristic crimson hue. But what happens to this vibrant red when oxygen is absent? Does it simply fade to a paler shade, or is there a more dramatic transformation?
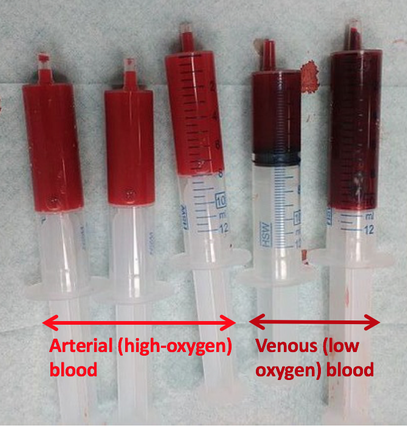
Image: qut.pressbooks.pub
Understanding the color of blood without oxygen goes beyond mere curiosity. It’s a fundamental concept in physiology, medicine, and even forensics. By grasping the intricate relationship between blood, oxygen, and color, we can glean insights into the health of our circulatory system, identify potential issues, and even solve mysteries.
The Role of Hemoglobin
At the heart of this fascinating phenomenon lies the molecule known as hemoglobin. This complex protein resides within our red blood cells, acting as a crucial oxygen transporter. Hemoglobin consists of four subunits, each containing a heme group—the iron-containing component responsible for binding oxygen.
When oxygen molecules attach to these heme groups, hemoglobin transforms into its oxygenated state, often referred to as oxyhemoglobin. This binding process causes a structural change in the hemoglobin molecule, resulting in the vibrant red color we associate with arterial blood.
The Deoxygenated State: From Red to Purple
Now, imagine a scenario where oxygen is scarce, such as in the tissues where oxygen is being consumed. As hemoglobin releases its oxygen molecules, it reverts back to its deoxygenated form known as deoxyhemoglobin. This shift in structure subtly alters the way this molecule interacts with light, leading to a change in color.
Deoxyhemoglobin, surprisingly, doesn’t simply fade to a paler red. Instead, it adopts a distinctly purplish hue. This purplish color is particularly noticeable in veins, where the blood is returning to the heart after delivering oxygen to the body’s tissues.
The change in color from red to purple may seem subtle, but it’s a crucial indicator of the blood’s oxygen saturation levels. The degree of redness or purple-ness in blood can be measured using a device called a pulse oximeter, which plays a vital role in medical diagnosis.
Beyond the Color: A Deeper Dive
The color of deoxygenated blood, however, is not merely a visual curiosity. It’s a phenomenon that reflects a dynamic interplay between hemoglobin, oxygen, and the surrounding environment. Several factors can influence the precise shade of deoxygenated blood, including:
- The concentration of hemoglobin: A higher concentration of hemoglobin in the blood results in a deeper, more vibrant color.
- The presence of other pigments: Bilirubin, a yellowish pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells, can impart a slight yellow tint to deoxygenated blood.
- The surrounding tissues: The color of deoxygenated blood can be influenced by the surrounding tissues, particularly in thin, translucent areas where the blood is visible through the skin.

Image: www.youtube.com
Real-World Applications: From Medicine to Forensics
The color of deoxygenated blood has significant practical applications in various fields. Physicians use it to assess the health of their patients. For example, a bluish discoloration of the skin (cyanosis) indicates a low oxygen saturation level, potentially due to respiratory or cardiovascular problems. In forensics, the color of blood stains can help investigators determine the timing of an injury.
Forensic scientists have developed techniques to assess the age of a bloodstain based on its color, taking into account factors like the drying process and the presence of oxygen. Understanding the changes in color due to oxygenation and deoxygenation helps to piece together the timeline of events.
What Color Is Your Blood Without Oxygen
Conclusion
The next time you gaze at a vein, remember that the purplish hue you see is a testament to the intricate relationship between blood, oxygen, and color. It’s a visual reminder of the vital role that oxygen plays in our bodies, and how the very color of our blood can provide vital clues about our health and even our history.
This journey into the world of deoxygenated blood has taken us beyond the realm of simple curiosity into the fascinating world of physiology, medicine, and forensics. The next time you witness this fascinating phenomenon, you’ll see it with a newfound appreciation for the hidden secrets it reveals.






