Imagine going on an expedition to the very heart of our planet. What would you find? Would it be a sea of molten rock, a realm of unimaginable pressure, or something entirely unexpected? The Earth, despite its familiar surface, hides a complex, layered structure that has fascinated scientists for centuries. This journey begins with a simple question: what lies beneath our feet? To uncover the secrets of Earth’s internal workings, we’ll explore a layers of the earth reading comprehension worksheet – a powerful tool for understanding our planet’s fundamental composition.

Image: laney-lee.com
This worksheet doesn’t just ask you to recall facts about the Earth’s layers – it encourages you to think critically about the relationships between these layers, how they influence both the surface and the environment, and how scientists use various methods to study something so inaccessible. It’s a journey where you actively engage with the information, making it stick in your mind and sparking further curiosity.
The Earth’s Layers: A Journey to the Core
1. Crust: The Thin Skin of our Planet
Our first stop is the Earth’s crust – the thin, outermost layer, like the skin of an apple. This is the solid ground we walk on, the ocean floor we explore, and the foundation for everything we see. It’s divided into two main types:
- Continental crust: Thicker, older, and less dense, it forms the continents. It’s mostly made of granite and other igneous rocks.
- Oceanic crust: Thinner, younger, and denser, it forms the ocean floor. It’s predominantly composed of basalt, a type of volcanic rock.
While the crust seems substantial, it’s incredibly thin compared to the rest of the Earth. Imagine a typical apple – the crust is only about as thick as the apple’s skin! Its thinness is what makes it so dynamic, constantly changing through tectonic plate movement, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes.
2. Mantle: The Hot and Flowing Heart
Beneath the crust lies the mantle, the Earth’s thickest layer. It’s made up of semi-molten rock called magma, which behaves like a very viscous fluid. Imagine honey – it flows, but slowly. The mantle’s heat, generated by radioactive decay deep within the Earth, creates convection currents. These currents like giant slow-moving rivers of magma, constantly circulate within the mantle, driving plate tectonics and shaping the Earth’s surface.
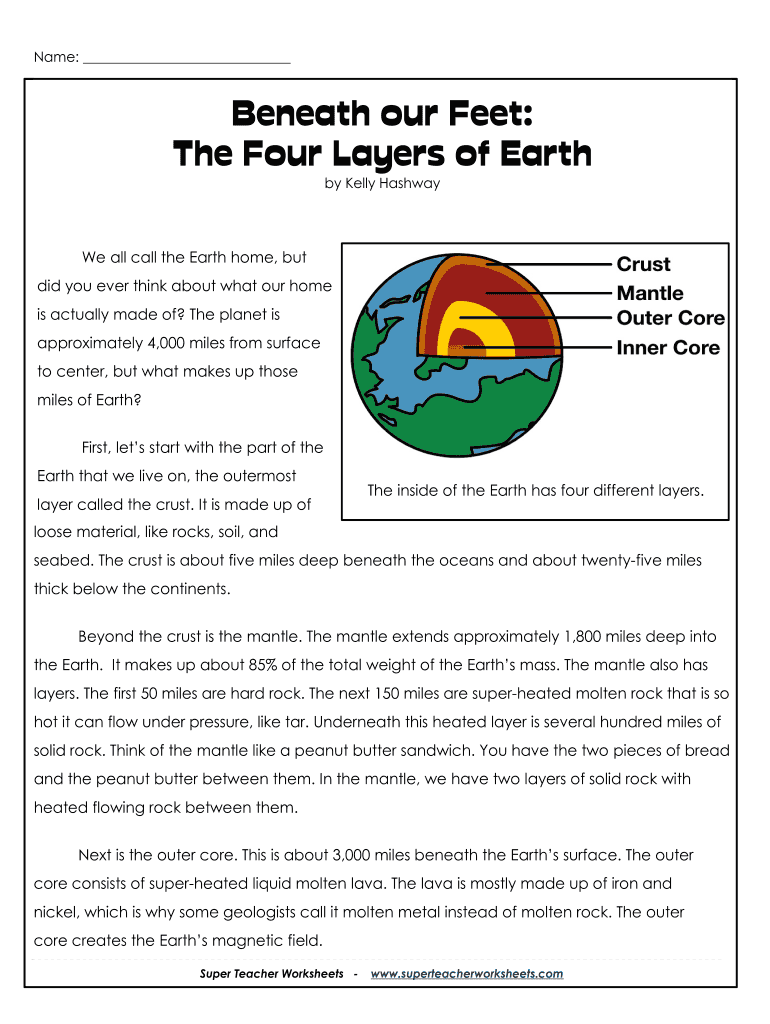
Image: ecoist70.blogspot.com
3. Outer Core: Molten Metal Seas
As we journey deeper, we encounter the outer core, a sphere of liquid iron and nickel. The intense pressure and heat cause the iron to melt, creating a churning, electrically charged sea. This molten metal is responsible for Earth’s magnetic field. Think of it as a giant bar magnet inside the Earth. This magnetic field acts as a shield, protecting us from harmful solar radiation coming from the sun.
4. Inner Core: A Solid Ball of Iron
At the very center of the Earth lies the inner core, a solid ball of iron and nickel. Despite the extreme pressure and unimaginable heat, the iron stays solid because of the immense pressure. This inner core, a testament to the Earth’s immense forces, creates a powerful gravitational pull that holds our planet together.
The Layers of the Earth Reading Comprehension Worksheet: Your Guide to Deeper Understanding
The layers of the earth reading comprehension worksheet doesn’t just provide facts; it helps you understand their significance. Questions might ask:
- How do the different layers interact?
- How do scientists use seismic waves to study the Earth’s interior?
- What are the implications of plate tectonics for geological events and life on Earth?
By working through these questions, you aren’t just memorizing information; you’re building connections and applying concepts. This approach goes beyond the mere memorization of facts, allowing you to truly internalize the knowledge, making it a part of your understanding of the Earth’s dynamic and fascinating history.
Putting Knowledge into Action: Real-world Applications
The knowledge gained from studying the Earth’s layers has numerous practical applications:
- Resource Exploration: Geologists use knowledge of the Earth’s layers to locate oil, gas, and mineral deposits.
- Earthquake Prediction: Understanding plate tectonics and the movement of the mantle aids in predicting earthquakes and mitigating their risks.
- Climate Change: The Earth’s layers play a crucial role in regulating climate, and this knowledge helps us understand the impact of human activities on our planet.
The Importance of Exploration: Unveiling the Secrets of Our Planet
Exploring the Earth’s layers is a continuous process. Scientists use various techniques, such as seismic waves, drilling, and satellite imagery, to uncover more information. Technological advancements continue to refine our understanding of the Earth’s internal structure. This ongoing research helps us understand the planet’s past, present, and future, guiding us towards sustainable practices and a better understanding of our place in the universe.
Layers Of The Earth Reading Comprehension Worksheet
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
The layers of the earth reading comprehension worksheet is more than just an educational tool – it’s a window into the Earth’s profound history and interconnectedness. By investigating the Earth’s layers, you gain an understanding of the processes that shape our world, the resources that sustain us, and the forces that have shaped life as we know it. So, embark on your own journey of discovery with the help of this worksheet, and delve deeper into the fascinating world beneath our feet.






