Have you ever wondered why some spaces have floor drains while others don’t? These inconspicuous but essential fixtures play a significant role in maintaining a safe and functional environment. Floor drains act as a vital safety mechanism, preventing water accumulation and potential flooding, especially in areas prone to spills or leaks. This article will delve into the intricate world of building codes and explore where floor drains are mandated by regulations, shedding light on their importance and ensuring a safer and more hygienic environment.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Building codes are designed to safeguard the well-being of occupants and structures. They establish minimum standards for construction, plumbing, and electrical systems, aiming to protect against hazards and ensure public safety. Floor drains are often incorporated into these codes, particularly in areas where the risk of water accumulation is high. Understanding these code requirements is crucial for homeowners, builders, and contractors alike, as it directly impacts the design and construction of various spaces.
Understanding the Importance of Floor Drains
Floor drains are essential for preventing water damage and maintaining hygiene in various settings. They serve as a crucial safety measure in:
1. Bathrooms and Kitchens
Floor drains in bathrooms and kitchens are essential for removing excess water from spills, leaks, or even heavy rainfall. Bathrooms are considered a high-risk zone for water accumulation due to showers, bathtubs, and sinks. Similarly, kitchens witness spills from cooking, dishwashing, and cleaning activities, making floor drains a vital safety component.
2. Basements and Garages
Basements and garages are susceptible to flooding due to heavy rainfall, leaking pipes, or even seepage from surrounding soil. Floor drains prevent water from accumulating, which can lead to mold growth, structural damage, and even health hazards.
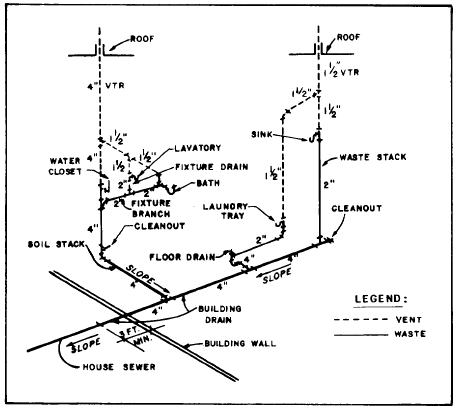
Image: jumpstarterdiscount.blogspot.com
3. Commercial and Industrial Facilities
Commercial and industrial settings often have unique requirements for floor drainage, depending on their intended use. Food processing areas, laboratories, and healthcare facilities, for instance, require specific floor drain designs and materials to ensure proper sanitation and hygiene.
Requirements Specified by Building Codes
Building codes differ slightly between jurisdictions, but they generally specify the following requirements for floor drains:
1. Location and Placement
Floor drains are typically positioned in the lowest point of a space to ensure efficient water drainage. In bathrooms, floor drains are often placed near the shower or bathtub, while in kitchens, they are located near sinks and dishwashers.
2. Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of the floor drain must be adequate to handle the anticipated flow of water. Building codes often specify minimum drain sizes based on the size and use of the space.
3. Material and Construction
Floor drains are typically made of durable materials like cast iron, stainless steel, or PVC. The design and construction of the drain must meet code requirements to ensure proper function and longevity.
4. Maintenance and Inspections
Building codes often include regulations for maintaining and inspecting floor drains. Owners are typically responsible for ensuring that drains are kept clean and free of debris. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to prevent clogs and ensure proper drainage.
Examples of Specific Code Requirements
Let’s delve into some specific code requirements for floor drains in different situations:
1. Residential Bathrooms
Most residential building codes mandate floor drains in bathrooms with a shower or bathtub. These codes may specify requirements for drain size, location, and the use of a trap to prevent sewer gases from entering the room.
2. Commercial Kitchens
Commercial kitchen regulations often impose stricter requirements for floor drains, considering the higher volume of water and potential for spills. Codes might specify drain size, the use of grease traps, and specific floor material choices to facilitate cleaning and sanitation.
3. Industrial Facilities
Industrial facilities with specialized operations, such as chemical processing plants or manufacturing units, face specialized code requirements regarding floor drains. These codes may require specific materials, drain designs, safety features, and regular inspections to ensure environmental safety and compliance.
Navigating Code Requirements and Consulting Professionals
Understanding and complying with building code requirements for floor drains can be complex. It’s recommended to consult with a licensed contractor, architect, or engineer knowledgeable about local regulations. These professionals can guide you through the specific requirements, design, and installation of floor drains, ensuring compliance and safety.
Where Are Floor Drains Required By Code
Conclusion
Floor drains may seem like an unassuming feature, but they play a crucial role in maintaining a safe and hygienic environment. Understanding building code requirements for floor drains is essential for ensuring the proper design and installation of these essential fixtures. From bathrooms and kitchens to garages and industrial facilities, floor drains safeguard against water accumulation, potential flooding, and health hazards.






